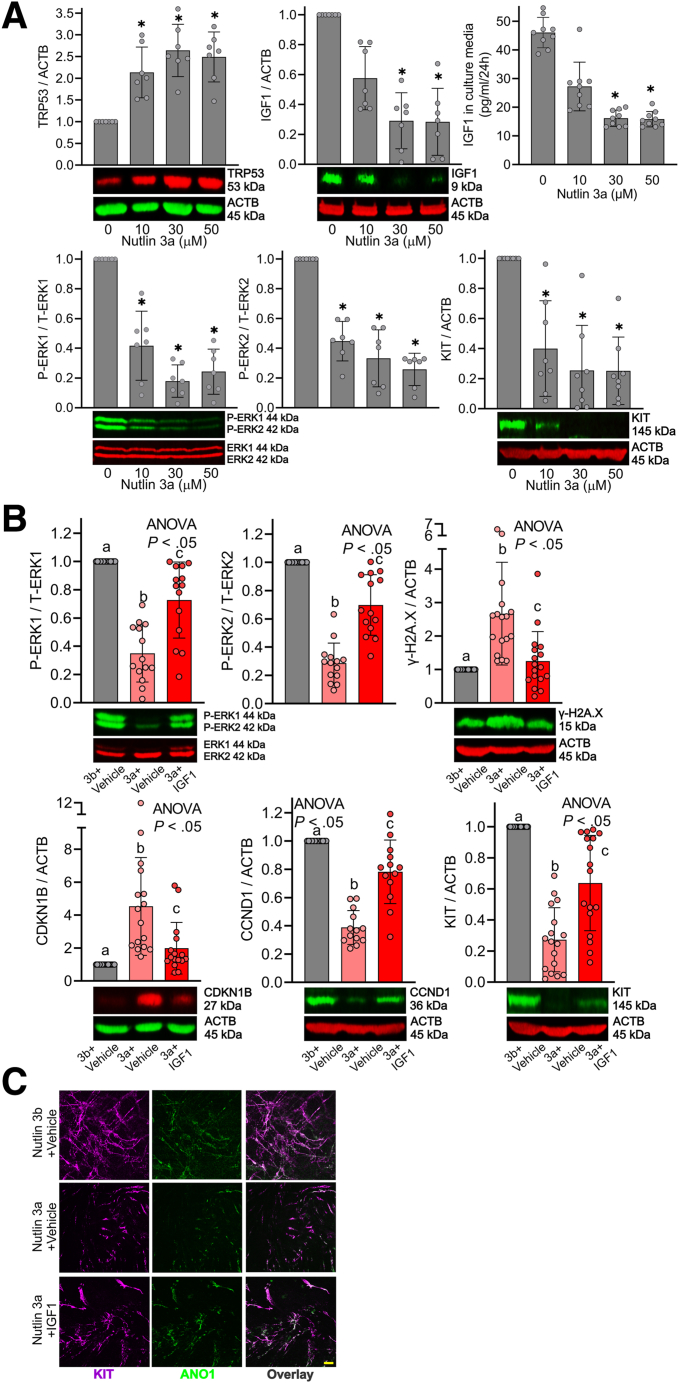
Figure 5.
Restoration of reduced ERK activation by IGF1 mitigates Trp53-induced ICC loss. (A) The Trp53 activator Nutlin 3a applied for 3 days dose-dependently increased TRP53 protein, and reduced IGF1 protein, ERK phosphorylation, and KIT protein by WB (n = 7–12/group) in gastric corpus + antrum tunica muscularis organotypic cultures from 12- to 14-day-old C57BL/6J mice. The same treatment dose-dependently reduced IGF1 secreted from gastric organotypic cultures by ELISA (n = 8/group). ACTB (actin beta) was used as a loading control. ∗P < .05 vs vehicle control (0 μmol/L) using Kruskal–Wallis 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA on ranks). (B) rhIGF1 (100 ng/mL) mitigated nutlin 3a–induced (30 μmol/L) reduced ERK phosphorylation (upper left panel), and DNA damage accumulation (upper right panel), increased CDKN1B (lower left panel), reduced CCND1 (lower right panel), and reduced KIT protein (lower right panel) in gastric corpus + antrum tunica muscularis organotypic cultures from 12- to 14-day-old C57BL/6J mice (n = 13–17/group). The inactive enantiomer nutlin 3b (30 μmol/L) served as a control for nutlin 3b. ACTB was used as a loading control. Statistical significance was determined using Kruskal–Wallis 1-way ANOVA (ANOVA on ranks). (C) Reduced gastric ICC networks by nutlin 3a (30 μmol/L) in gastric corpus + antrum tunica muscularis organotypic cultures from 12- to 14-day-old C57BL/6J mice were restored by rhIGF1 treatment. Representative confocal stacks showing KIT+ (magenta) and ANO1+ (green) ICC in corresponding regions of the gastric corpus (greater curvature, full thickness) of nutlin 3b (30 μmol/L) + vehicle, nutlin 3a (30 μmol/L) + vehicle, and nutlin 3a (30 μmol/L) + rhIGF1 (100 ng/mL). n = 3/group. Scale bar: 10 μm.