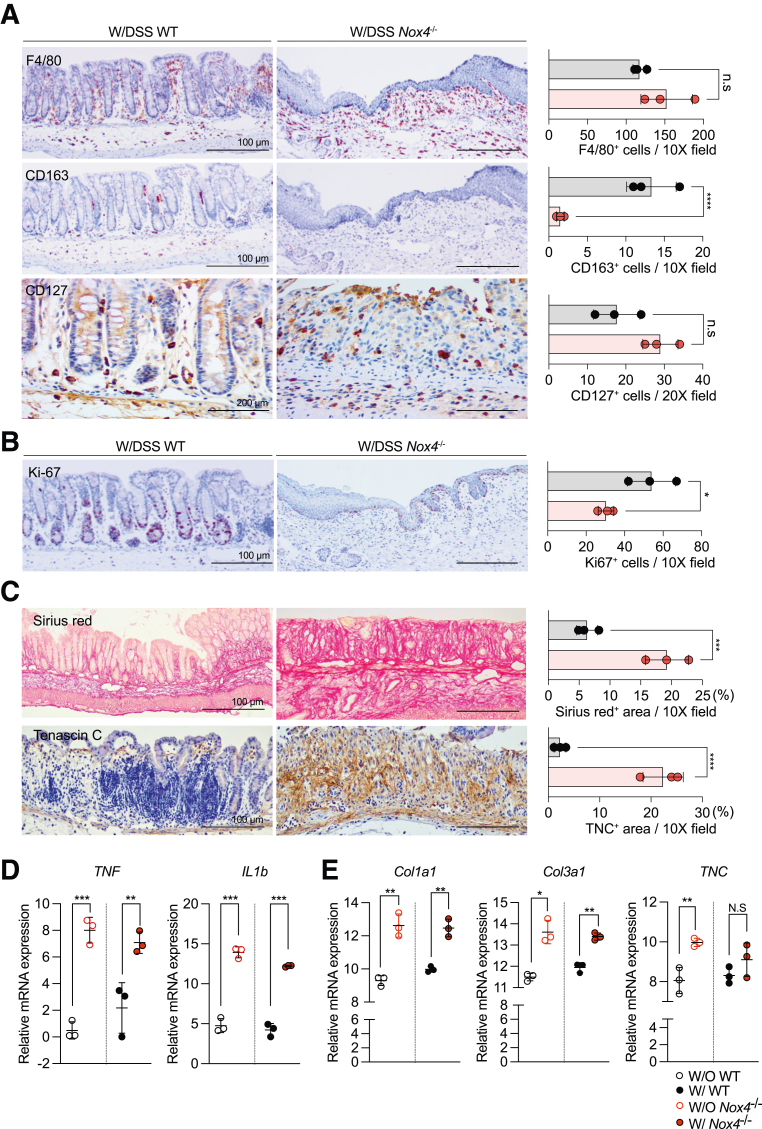
Figure 3.
Nox4 is involved in intestinal fibrosis and immune-mediated tissue regeneration. (A) Immunohistochemistry with antibodies against F4/80 (top) indicating M1 macrophages, CD164 (middle) indicating M2 macrophages, and CD127 (bottom) indicating lymphoid cells on DSS-treated WT and Nox4-/- mouse colon sections. (B) Immunohistochemistry with antibody against Ki-67 indicating proliferating cells. (C) Sirius red staining showing the fibrotic area in red (top). Immunolabeling with antibodies against Tenascin-C indicates fibrosis in the colon tissue (bottom). Each positive staining area was measured by ImageJ and shown as a bar graph. Grey, WT group (N = 3); red, Nox4-/- group (N = 3). (D) Reverse-transcription quantitative PCR results of proinflammatory-related genes TNF, and IL1b. (E) Reverse-transcription quantitative PCR results of fibrosis-related genes Col1a1, Col3a1, and TNC. Data are expressed as means ± SD. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .005, and ∗∗∗∗P < .001 compared with WT. Ki-67, marker of proliferation Ki(Kiel)-67.