Figure 3.
Expansion and clusteringof TPS genes in J. sambac genome
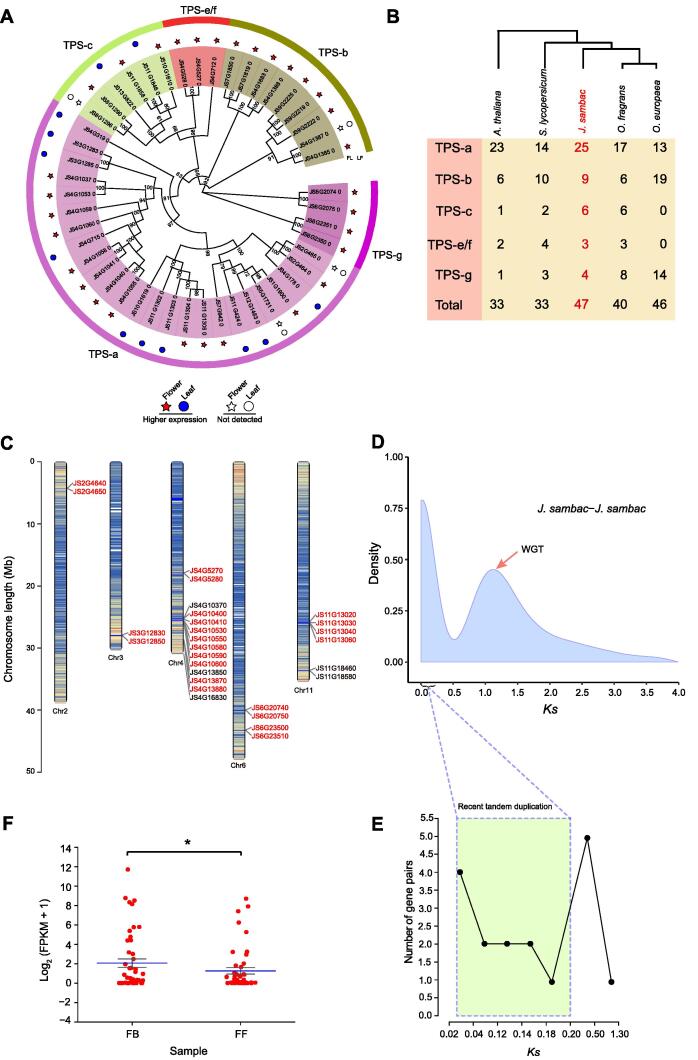
A. Phylogenetic tree of the 47 TPS genes containing two conserved domains identified in the J. sambac genome. Colored stars and circles indicate the TPS genes highly expressed in flowers (FBs and FFs) and leaves, respectively. The expression level of each TPS gene is presented in Table S12. TPS protein sequences were aligned using Clustal X (version 2.0), and the phylogenetic tree was constructed using IQ-TREE (version 1.6.9) by the maximum likelihood method with bootstrap values of 1000 replicates. The black numbers beside the branches represent bootstrap values. B. Number of TPS genes containing two conserved domains in J. sambac, A. thaliana, S. lycopersicum, O. fragrans, and O. europaea. C. Chromosomal distribution of the J. sambac TPS genes. The colored lines in different chromosomes indicate the gene density; darker lines indicate higher gene density. Red gene IDs indicate TPS genes that form gene clusters on chromosomes. The chromosomal distribution of TPS genes was illustrated with TBtools. D.Ks distribution of the paralogous TPS genes in the J. sambac genome. E. The TPS gene pairs (paralogs) in the box had Ks < 0.2. F. Expression levels of TPS genes in FBs and FFs of J. sambac. Blue bars indicate the mean expression levels. *, P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). TPS, terpene synthase; FPKM, fragments per kilobase million; Ks, synonymous substitution rate.