Fig. 1.
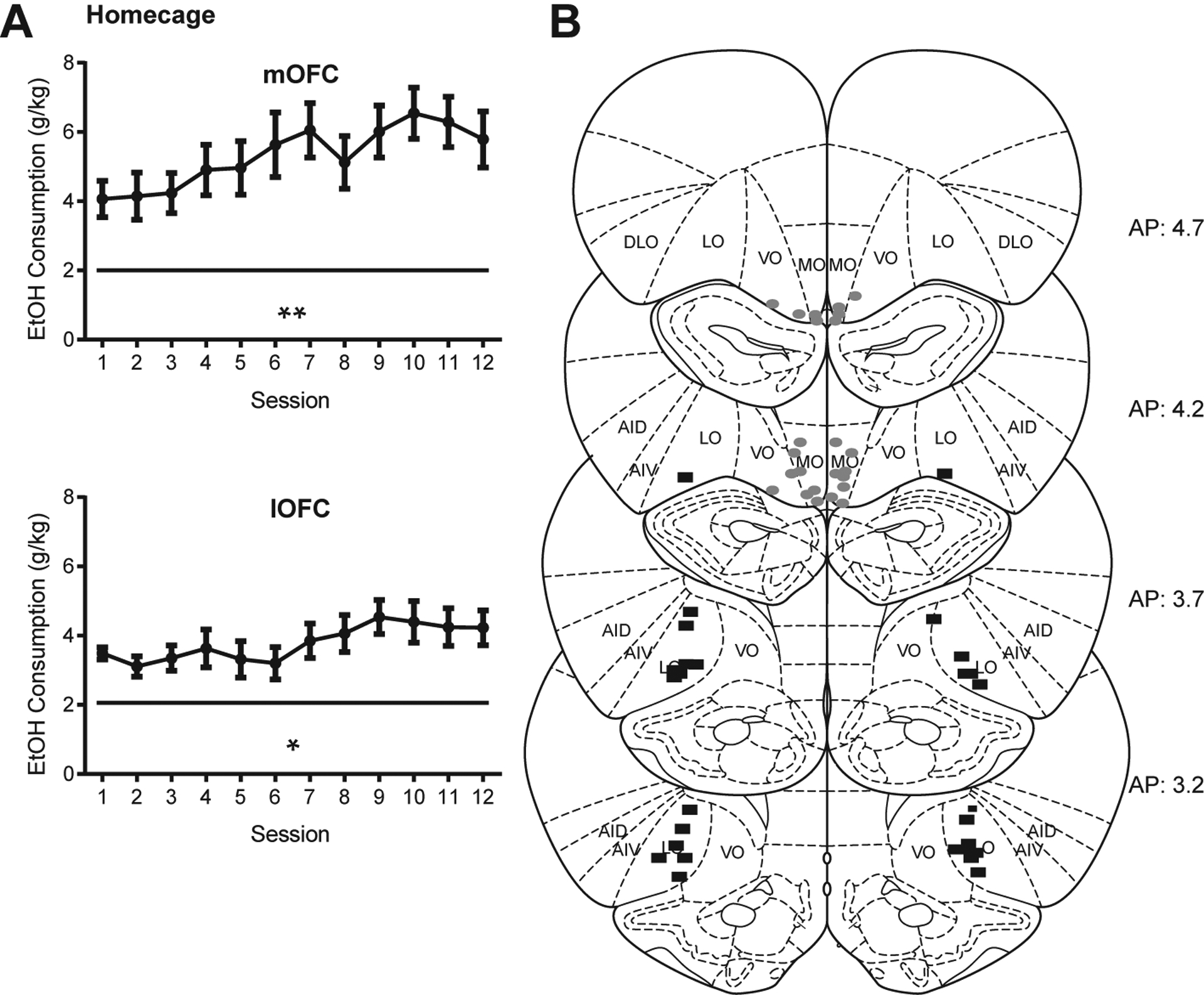
(A) Rats increased drinking over the course of homecage intermittent access. Mean ± SE EtOH in-take in g/kg on each drinking day over the course of 4 weeks of homecage drinking (pre-cannula implant) for mOFC implanted rats (n = 16, top) and lOFC implanted rats (n = 16, bottom). Significant effects observed across all animals (F(11, 341) = 5.97, p < 0.0001, mixed-effects model with Geisser-Greenhouse correction, main effect of drinking session) and within each group (mOFC (F(11, 165) = 4.00, p = 0.007) and lOFC (F(11, 165) = 2.84, p = 0.027, repeated-measures ANOVAs). See main text for additional analyses. (B) Cannula placements based on damage caused by injector cannulae. Gray ovals = mOFC placements. Black rectangles = lOFC placements. One rat was removed due to missed cannula placements. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
