Table 2. Data Sets Used for Traininga.
| Name | Nhot | Nhot positions | Lmaxb | |AA|c | Search spaced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 4 | F19,W57,Y150,F85′ | 4 | 20 | 1.6 × 105 |
| D2 | 6 | F19,W57,Y150,A228,R415,F85′ | 6 | 20 | 6.4 × 107 |
| D3 | 8 | F19,W57,Y150,V225,A228,R415,F85′,F86′ | 8 | 20 | 2.56 × 1010 |
| D4 | 8 | F19,W57,Y150,V225,A228,R415,F85′,F86′ | 4 | 20 | 1.12 × 107 |
| D5 | 4 | F19,W57,Y150,F85′ | 4 | 10 | 1 × 104 |
The number of examples per data
set is 10,000 variants. 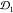 is the main data set used in this study,
it contains mutants of degrees 1, 2, 3, and 4 (Lmax = 4) in 4 positions (Nhot = 4) that are allowed to mutate to any of the 20 standard
amino acids (|AA| = 20). The search space of
is the main data set used in this study,
it contains mutants of degrees 1, 2, 3, and 4 (Lmax = 4) in 4 positions (Nhot = 4) that are allowed to mutate to any of the 20 standard
amino acids (|AA| = 20). The search space of 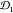 is therefore 1.6 × 105.
Data set
is therefore 1.6 × 105.
Data set  (Lmax = 8, Nhot = 8) also resembles conditions relevant
in enzyme design campaigns, with a search space of 2.56 × 1010. In all cases, ligand is E4.
(Lmax = 8, Nhot = 8) also resembles conditions relevant
in enzyme design campaigns, with a search space of 2.56 × 1010. In all cases, ligand is E4.
Maximum allowed mutant degree. Lmax = 4, means that single (L = 1), double (L = 2), triple (L = 3), and quadruple (L = 4) mutants were allowed.
The number
of amino acids allowed
as target mutation, |AA|, was reduced to 10 in 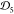 : AA = {A,C,D,E,G,H,I,K,L,M}, to see if the trained model could generalize to unseen amino acids,
i.e., AA = {F,N,P,Q,R,S,T,V,W,Y}.
: AA = {A,C,D,E,G,H,I,K,L,M}, to see if the trained model could generalize to unseen amino acids,
i.e., AA = {F,N,P,Q,R,S,T,V,W,Y}.
The search space for each data set was calculated with the following formula: C(Nhot,L)·|AA|L, where C(Nhot,L) is the combination of L items (mutant degree) taken from the set of size Nhot (number of hotspots), and |AA| is the number of amino acids allowed (normally 20).
