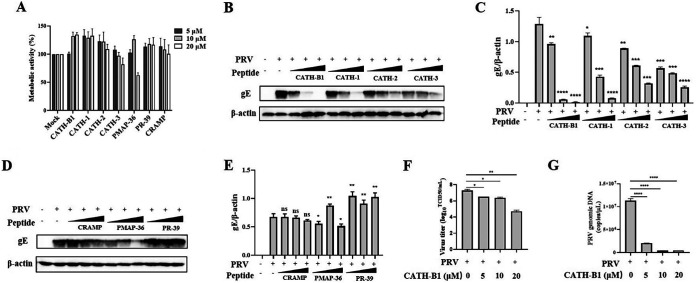
FIG 1.
Screen of antimicrobial peptides derived from cathelicidins inhibiting pseudorabies (PRV) infection in PK-15 cells. PK-15 cells were treated with seven different peptides in different concentrations (5, 10, and 20 μM). After 2 h, the cultures were washed, and the cells were incubated in fresh medium for another 22 h. (A) Cell viability was determined by the WST-1 assay. The results are the averages ± SD of experiments performed in triplicate. PK-15 cells were infected with PRV at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1 and then simultaneously treated with chicken-derived peptides CATH-B1 and CATH-1, -2, and -3 and peptides CRAMP, PMAP-36, and PR-39 derived from other animals at different concentrations (5, 10, and 20 μM), respectively. (B to E) After 24 h, PRV glycoprotein E (gE) protein levels were detected by Western blotting (B and D) and analyzed by ImageJ (C and E). In all cases, β-actin was used as a loading control, and the blots were representative of three independent experiments. (F, G) Meanwhile, the averages ± SD of virus titers in duplicate were determined by the 50% tissue culture infective dose (TCID50) assay (F) and that of viral genomic DNA in triplicate was calculated by the qPCR method (G). Student’s t tests were used for statistical analyses. ns, no significance; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001, comparing the PRV-treated group to the PRV plus CATH-B1-treated groups. CRAMP, cathelicidin-related AMP.