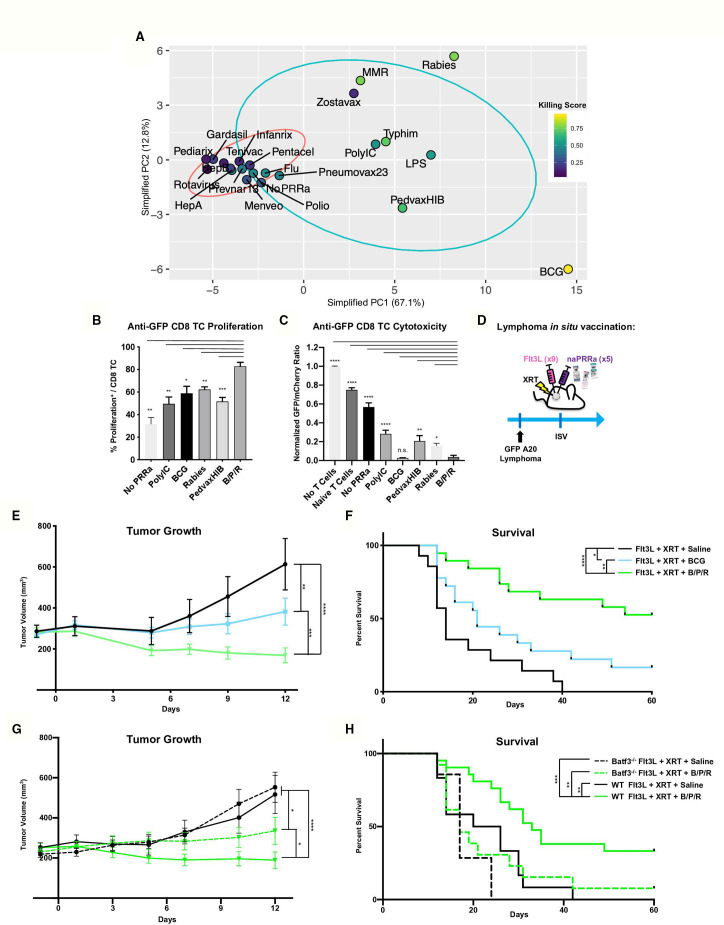
Figure 4.
Rational naPRRa combinations are superior to single agent vaccines in vivo and partially dependent on Batf3 DC. (A) PCA was performed using only phenotypic markers that significantly correlated with T-cell cytotoxicity identified in online supplemental figure 6a. (B, C) Cross-presentation assay was performed, comparing the B/P/R combination versus individual naPRRa and synthetic PRRa. Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. (d) Schema of murine preclinical lymphoma ISV model. GFP-A20 lymphoma-bearing mice were treated intratumorally with Flt3L. Tumors were then locally XRT, and naPRRa or saline was injected intratumorally. Mice were monitored for tumor growth (E) and survival (F). Data pooled from three independent experiments, n=20–25 mice per group. Statistical significance was calculated by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (G, H) Murine preclinical lymphoma ISV model was performed with WT vs Batf3-/- mice. Animals were monitored for tumor growth (G) and survival (H). Statistical significance was calculated by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Data pooled from two independent experiments, n=10–20 mice per group. ANOVA, analysis of variance; DC, dendritic cells; ISV, in situ vaccination; PCA, principal component analysis; PRRa, pattern recognition receptor agonists.