Figure 1. NIHTB and PROMIS captured the poorer emotional and motor health in PASC participants compared to controls.
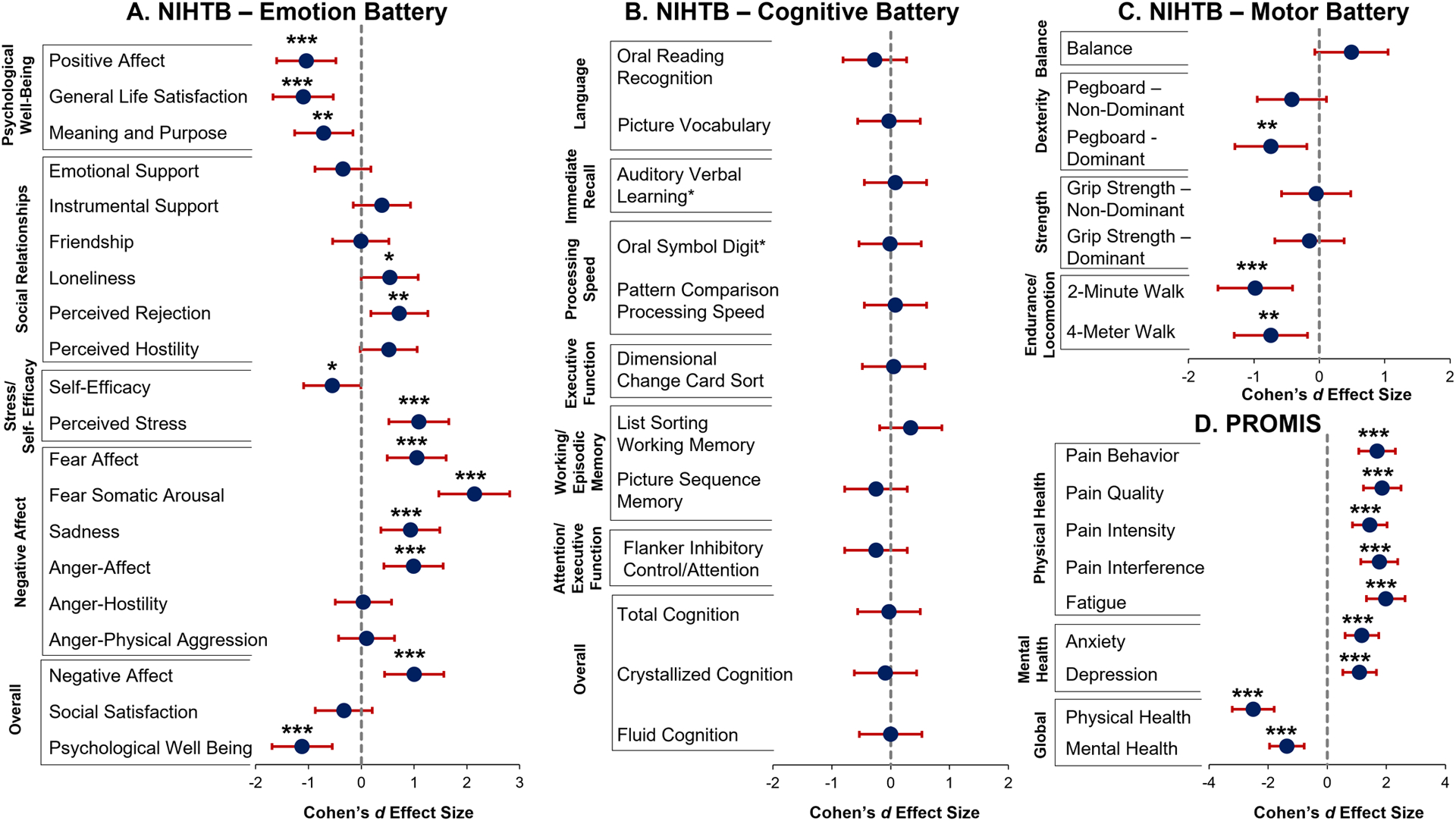
All NIHTB assessments were administered in person by trained researchers using an iPad. NIHTB Emotional (NIHTB-EB), Cognitive (NIHTB-CB), and Motor (NIHTB-MB) batteries used the iPad NIH Toolbox App (v.1.23.4300) and PROMIS(3) surveys used REDCap. Domains and selected surveys are in the Supplement. All statistical analyses were performed using R (v.4.1.2). Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), covaried for age, evaluated group (PASC vs. controls) differences on NIHTB and PROMIS T-Scores (corrected for age, sex, education, race/ethnicity) and Oral Symbol Digit and Auditory Verbal Learning raw scores. Cohen’s d effect sizes with 95% Confidence Intervals were calculated using the package ‘effsize’. For this exploratory study, significance was set at p<0.05.
* p≤0.05, ** p≤0.01, *** p≤0.001
