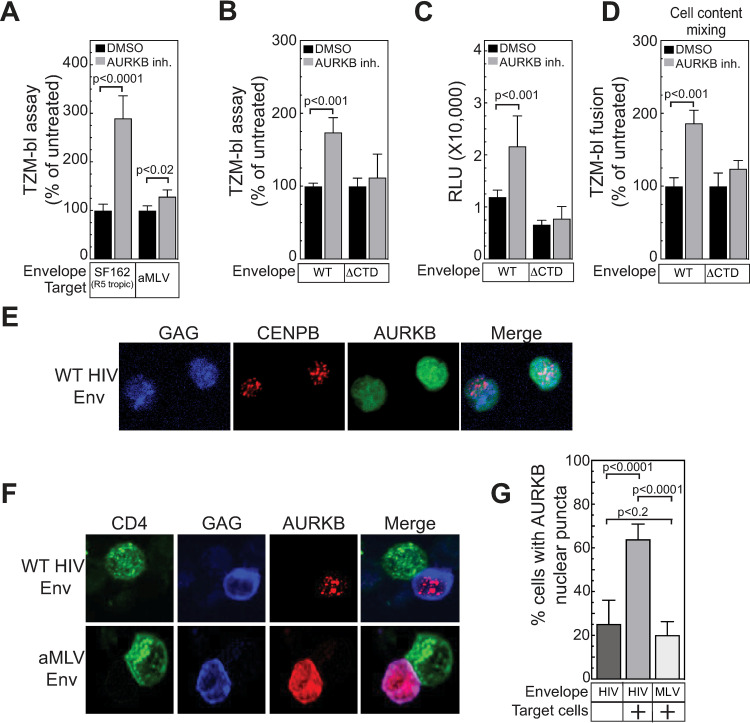
Fig 6. Interaction of WT HIV Env-expressing cells with CD4+ cells relocalizes AURKB to nuclear puncta.
(A) The effect of AURKB inhibition (Hesperidin, 5 μM) on viral spread was determined as described in Fig 4, except the CCR5 tropic envelope from HIV-1 strain SF162 or the envelope from amphotropic MLV was used instead of the envelope from the CXCR4 HIV-1 strain NL4-3. (B) The effect of AURKB inhibition (Barasertib, 20 μM) on viral spread was determined as described in Fig 4 with cells expressing the NL43 genome and either the WT envelope or a variant lacking the cytoplasmic tail domain (ΔCTD) derived from the envelope of CXCR4 HIV-1 strain NL4-3. (C) The firefly luciferase activities from the experiment in (B) are reported as raw, unprocessed relative light units (RLU) instead of normalized to 100%. (D) The effect of AURKB inhibition (Barasertib, 20 μM) on syncytia formation was determined as described in Fig 5G with cells expressing HIV-1 TAT and either the WT envelope or a variant lacking the cytoplasmic tail domain (ΔCTD) derived from the envelope of CXCR4 HIV-1 strain NL4-3. The data shown in (A-D) are the average mean values obtained in an experiment performed with quadruplicate samples and are representative of three independent experiments. (E) HIV producer cells (Jurkat) were transfected with a plasmid encoding mCherry-AURKB and plasmids containing an HIV genome encoding fluorescent protein (CFP) fused to HIV-gag, and a plasmid WT HIV envelope and were allowed to settle to a poly-D-lysine slide for 20 minutes, fixed, mounted and imaged by confocal microscopy with a 60X objective. (F) HIV producer cells (Jurkat) were transfected with a plasmid encoding mCherry-AURKB and plasmids containing an HIV genome encoding fluorescent protein (CFP) fused to HIV-gag, and plasmids encoding either amphotropic MLV or WT HIV envelope and mixed with target cells (SupT1) expressing fluorescent CD4 (CD4-YFP) for 20 minutes, fixed, mounted and imaged by confocal microscopy with a 60X objective.(G) Total AURKB localization at nuclear puncta by WT HIV-1 or MLV envelope after mixing with target cells. 10 individual fields were counted and transfected cells with AURKB puncta were counted. The data shown are the average mean values from 10 independent fields and are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of the data in all panels. P-values were calculated using a standard Student’s t-test and significant changes relative to DMSO treated or no target cell controls are indicated.