Fig. 1.
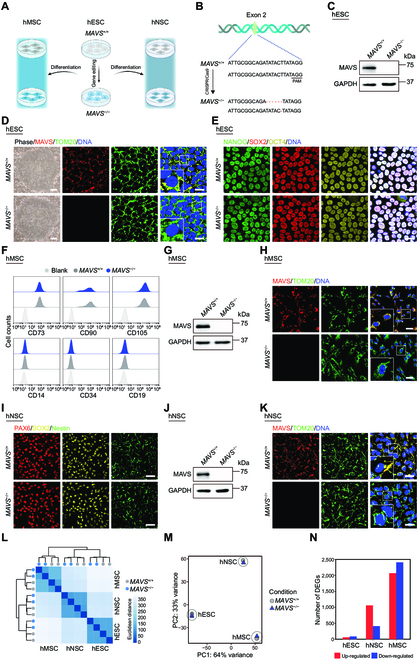
Generation and characterization of MAVS-deficient pluripotent stem cells. (A) Schematic workflow showing the generation of MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hMSCs and hNSCs from hESCs. (B) Schematic illustration of MAVS gene editing in exon 2 using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated nonhomologous end joining in hESCs. (C) Western blotting analysis of MAVS protein in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hESCs. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (D) Left: Phase-contrast images of MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hESCs. Scale bar, 250 μm. Right: Immunofluorescence staining of MAVS and TOM20 in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hESCs. Scale bar, 25 μm. Insets show the zoomed-in images. (E) Immunofluorescence staining of pluripotency markers NANOG, SOX2, and OCT4 in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hESCs. Scale bar, 25 μm. (F) FACS analysis of canonical markers of hMSCs, including CD73, CD90, and CD105, as well as irrelevant markers CD14, CD19, and CD34 in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hMSCs. Cells unstained were used as the blank control. (G) Western blotting analysis of MAVS protein in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hMSCs. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (H) Immunofluorescence staining of MAVS and TOM20 in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hMSCs. Scale bar, 50 μm. Insets show the zoomed-in images. (I) Immunofluorescence staining of hNSC markers PAX6, SOX2, and Nestin in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hNSCs. Scale bar, 25 μm. (J) Western blotting analysis of MAVS protein in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hNSCs. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (K) Immunofluorescence staining of MAVS and TOM20 in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hNSCs. Scale bar, 25 μm. Insets show the zoomed-in images. (L) Heatmap showing the Euclidean distance between replicates of RNA-seq in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/−hESCs, hNSCs, and hMSCs. The color key of the Euclidean distance from blue to white indicates strong to weak correlation. (M) Principal component (PC) analysis showing the reproducibility of RNA-seq between replicates in MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hESCs, hNSCs, and hMSCs. (N) Bar plot showing the number of up-regulated (red) and down-regulated (blue) DEGs between MAVS+/+ and MAVS−/− hESCs, hNSCs, and hMSCs.
