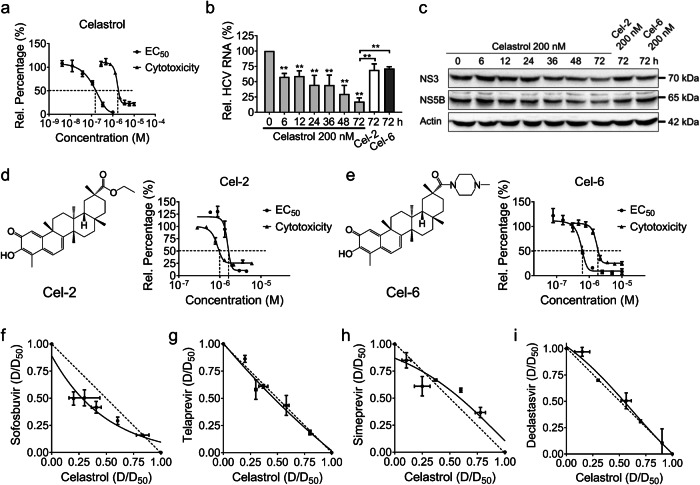
Fig. 3. Celastrol exhibited a potent inhibitory effect against HCV in Huh-luc/neo-ET genotype 1b replicon cells.
a The anti-HCV activity and cytotoxicity of celastrol. b The relative expression level of HCV RNA with the treatment of celastrol, Cel-2, and Cel-6 for up to 72 h. c The expression levels of HCV NS proteins with the treatment of celastrol, Cel-2, and Cel-6 for up to 72 h. The anti-HCV activity and cytotoxicity of (d) Cel-2 and (e) Cel-6. Huh-luc/neo-ET cells were co-incubated with various concentrations of celastrol alone or with (f) Sofosbuvir, (g) Telaprevir, (h) Simeprevir, and (I) Daclatasvir at different potency ratios for 72 h. Ratios of the apparent EC50 of each drug in combination with its EC50 when applied alone were plotted against each other in isobolograms. The hypotenuse represented the linear additive response to the action of two drugs. Isoboles that bow below the hypotenuse indicate synergism, and isoboles that bow above the hypotenuse indicate antagonism. Experimental data points on the isobole represent a combination that inhibits the HCV replication by 50% and is hence isoeffective with the line of additivity. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD (**P < 0.05).