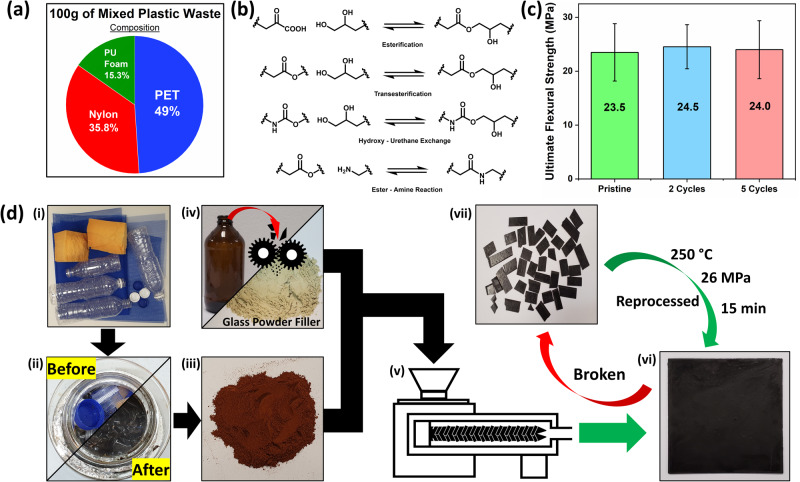
Fig. 4. Application of vitrimerisation to upcycle mixed plastics.
Demonstration of the potential feasibility of this work, on mixed plastic waste. a Composition of simulated mixed plastic waste for this demonstration, based on an existing study2 on waste composition. b A series of chemical reactions that may occur to facilitate crosslinking and vitrimerisation. c Flexure strength of composite after 2 cycles and 5 cycles of reprocessing compared to the pristine sample. Error bars were produced due to sample variations during the 3-point flexural bend. d Scheme for the plastic waste upcycling process. (i) Actual plastic waste for depolymerization was shredded and placed into a reaction vessel. (ii) Plastic waste placed in a reaction vessel (Before) was solubilized in solvent at 180 °C forming a dark slurry (After) after 20 min. (iii) A red precipitate was achieved which was washed and collected as recovered mixed plastic (RMP). (iv) A waste glass beverage bottle was ground into powder particles, with a diameter of approximately 150 microns. (v) 80 wt% of waste glass powder was extruded with RMP at 220 °C at 80 rpm. (vi) The extruded sample was hot pressed to afford a 12 cm × 12 cm square tile. (vii) The resultant tile is reprocessable. The tile was broken apart and can be reformed when hot-pressed at 250 °C and 20 MPa for 15 min.