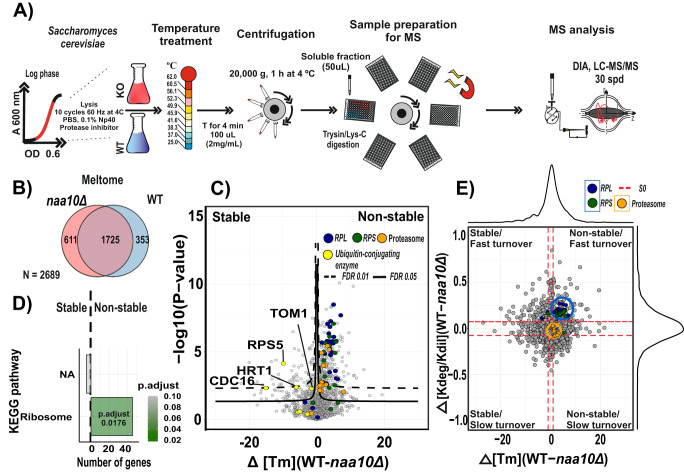
Fig. 6. Ribosomal proteins are unstable and rapidly degraded in NatA-defective yeast cells.
A Schematic representation of the implemented TPP-DIA strategy. Yeast cells grown in mid-log phase were harvested by centrifugation and submitted to a temperature treatment. Lysates were digested using Lys-C and trypsin. Quantification was performed by using label-free intensities (LFQ; label-free quantitation). n = 6 replicate cultures per condition. Melting curves were inferred by using a four-parameter log-logistic model. B Venn diagram depicting numbers of all protein-melting temperatures, (Meltome, n = 2689). C Comparison of the WT and naa10Δ strains in a volcano plot to identify changes in protein-melting temperature. Significant regulated proteins at 1% and 5% false discovery rate (FDR) are delimited by dashed and solid lines, respectively (FDR controlled, two-slide t test, randomizations = 250, s0 = 0.1). D GSEA-based KEGG pathway enriched analysis. P values were calculated by two-sided permutation test and multiple hypothesis testing was FDR corrected. Significance threshold set at FDR > 0.05 Significance threshold set at P.adjust <0.05, NA: no enriched terms at the specified cutoff. E Scatterplot representing the overlap between protein thermostability and degradation. Dashed red line delineate the minimal fold change (s0, 0.1). Melting temperature and degradation difference distribution are shown in the top and right plot border, respectively. Source data are provided as a Source Data file (C, E).