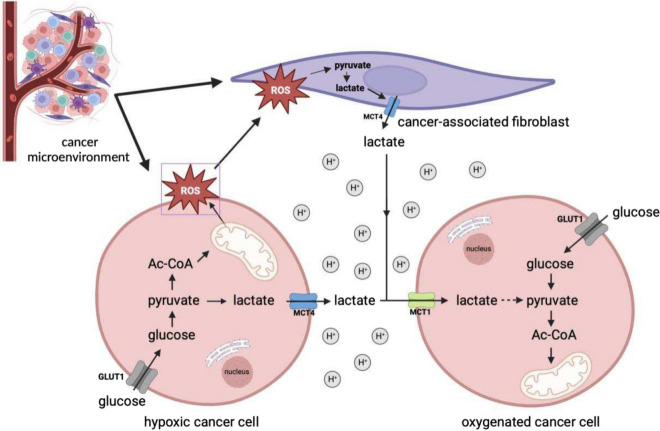
Fig. 3.
Reverse Warburg effect. In the reverse Warburg effect, oxidative cancer cells can take up lactate from hypoxic cancer cells. Moreover, oxidative cancer cells induce oxidative stress in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) by secreting reactive oxygen spiecies (ROS), which in turn triggers the aerobic glycolysis in CAFs. In consequence, lactate and pyruvate produced by CAFs are metabolized in adjacent oxidative cancer cells. AC-CoA acetyl coenzyme A