Figure 5.
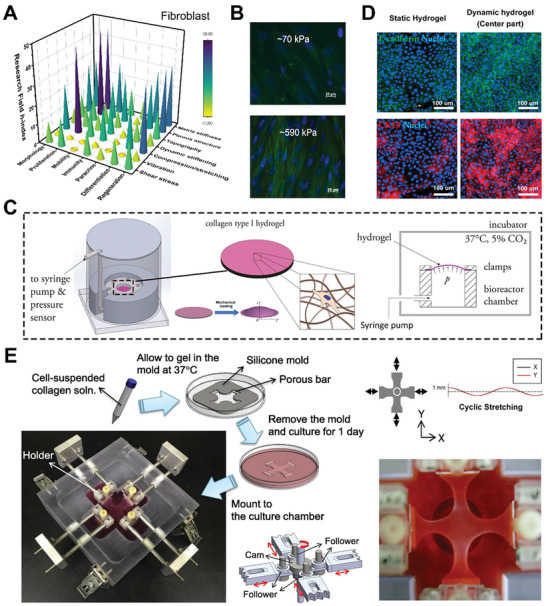
Mechanical stimulation on fibroblast cell behaviors by hydrogel‐based platforms. A) 3D bar graph of mechanical stimulation on fibroblast for various cell activities and biomedical applications. The research conditions are evaluated based on h‐index of each field were calculated by paper publication and citation data from Scopus. B) Fluorescent staining indicates that fibroblasts, which cultured in matrix with higher stiffness, express more α‐smooth muscle actin (α‐SMA). The cells are detected by staining the cell nucleus (blue DAPI) and α‐SMA (fluorescent green). Reproduced with permission.[ 213 ] Copyright 2012, Elsevier. C) Schematic illustration of dynamic pump‐based bioreactor that applies tension to deform installed hydrogels. Reproduced with permission.[ 227 ] Copyright 2021, Elsevier. D) Whole‐mount staining for E‐cadherin and CK19 expression suggests that dynamic forces can promote the early maturation of the dermo–epidermal skin substitute. Adapted with permission.[ 227 ] Copyright 2021, Elsevier. E) Schematic and working procedure of the cyclic four‐arm stretcher. The fibroblast‐seeded hydrogel is installed in the chamber and stretched by dynamic actuator system. Adapted with permission.[ 231 ] Copyright 2018, Elsevier.
