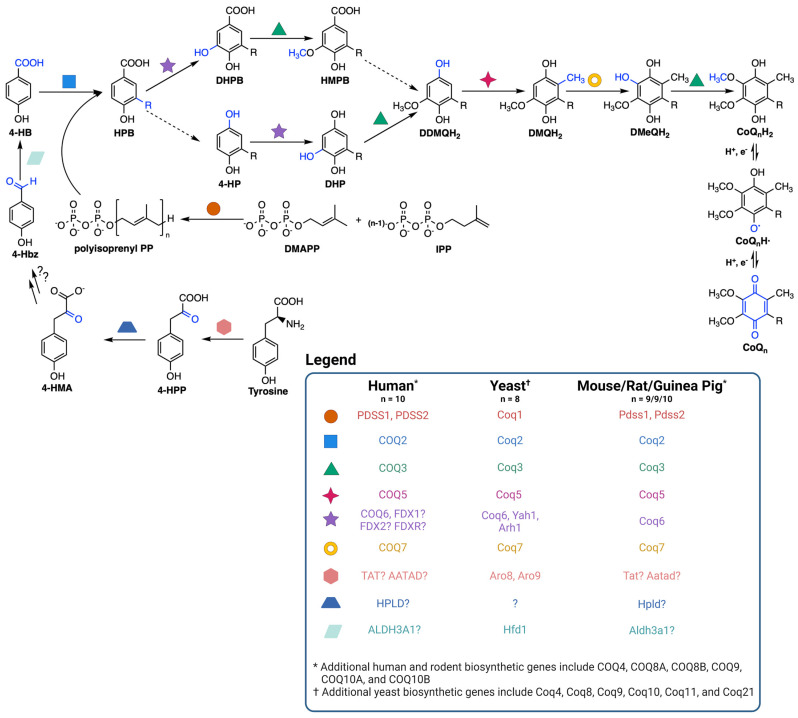
Figure 2.
Coenzyme Q biosynthetic pathway. The dashed arrows indicate decarboxylation and hydroxylation steps that are catalyzed by unknown enzyme(s), thus resulting in an uncertainty in the order of reactions. Intermediates in the pathway include 4-HPP, 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate; 4-HMA, 4-hydroxymandelate; 4-Hbz, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde; 4-HB, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid; DMAPP, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate; IPP, isopentenyl pyrophosphate; HPB, 4-hydroxy-3-polyprenyl-benzoic acid; DHPB, 4,5-dihydroxy-3-polyprenylbenzoic acid; HMPB, 4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-3-polyprenylbenzoic acid; DHP, 4,5-dihydroxy-3-polyprenylphenol; DDMQH2, 2-methoxy-6-polyprenyl-1,4-benzohydroquinone; DMQH2, 2-methoxy-5-methyl-6-polyprenyl-1,4-benzohydroquinone; DMeQH2, 3-methyl-6-methoxy-2-polyprenyl-1,4,5-benzenetriol; n is the number of isoprene units in the polyisoprenyl tail. Yeast can also utilize p-aminobenzoic acid as a ring precursor, and its prenylation by Coq2 produces the early intermediate 4-amino-3-polyprenyl-benzoic acid (HAB, [38]). Adapted with permission from Wang et al. [44]. Created with Biorender.com (accessed on 28 June 2023).