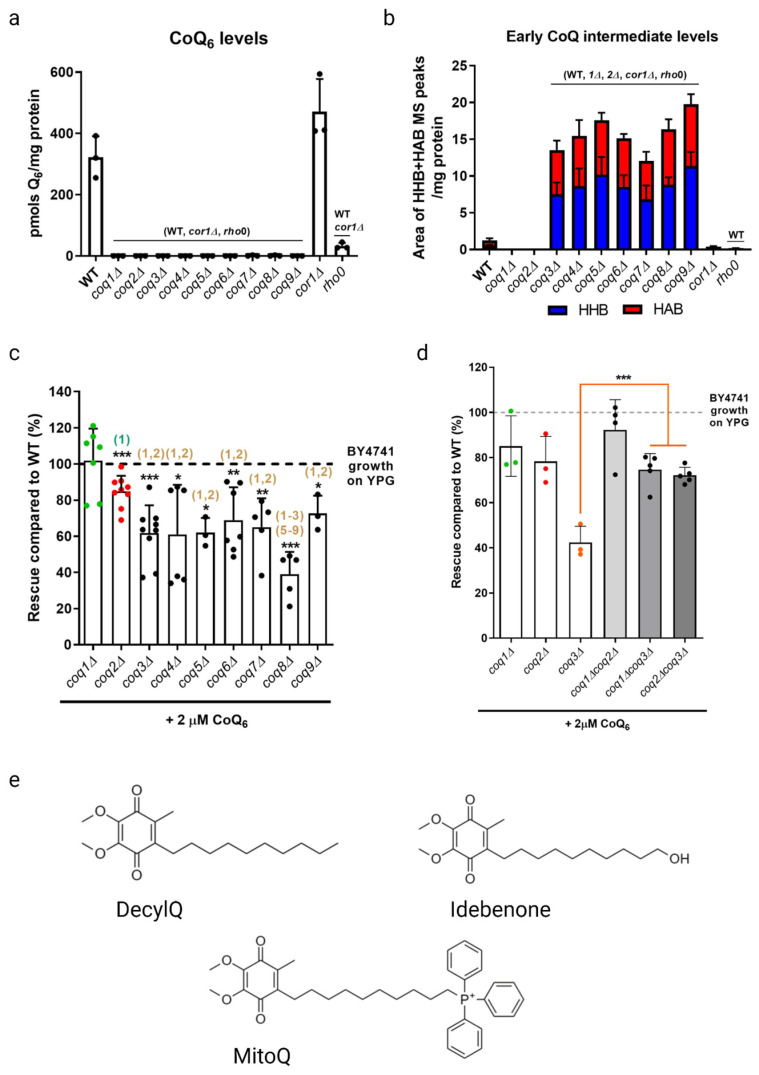
Figure 3.
Yeast coq mutants are rescued with exogenous CoQ6 but not non-isoprenoid CoQ analogues. (a) CoQ6 was not detected in any of the coqΔ mutants. CoQ6 (pmol/mg protein) was determined based on a CoQ6 standard curve as described in (Tsui et al., 2019). (b) Each of the coq mutants, from coq3Δ to coq9Δ, accumulated early CoQ6 intermediates (HHB and HAB). The amount of HHB and HAB was calculated as the area of the MS peak/mg protein. (c) Yeast mutants harboring deletions in either the COQ1 or COQ2 gene showed more robust rescue in response to exogenous CoQ6 treatment than do the other single coq null mutants (coq3Δ–coq9Δ). (d) Additional deletions of either COQ1 or COQ2 restored the deficient CoQ6-rescue of a coq3Δ mutant, but do not affect the phenotype observed in coq1Δ or coqΔ2 strains. Columns represent the degree of rescue (in %) ± SD of a strain compared to WT, which is defined as 100% and represented as a dashed line. Statistically significant differences between a specific coqΔ mutant and one of its counterparts (another coqΔ mutant) are denoted with numbers in parentheses on top of the columns. (1) represents differences comparing to coq1Δ, (2) represents differences comparing to coq2Δ, (3) represents differences comparing to coq3Δ, etc. Three or more independent rescue experiments were performed for every strain. Asterisks on top of the columns represent significant differences when compared to WT (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). (e) Structures of CoQ analogues. Panels (a–d) reproduced with permission from Fernandez-del-Rio et al. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, published by Elsevier, 2020 [18]. Created with Biorender.com (Accessed on 27 June 2023).