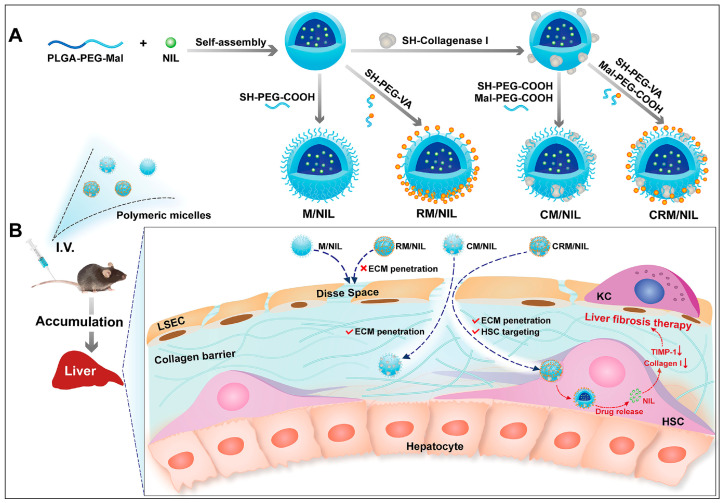
Figure 4.
(A) Schematic representation depicting the process involved in the preparation of four distinct polymeric micelles. The surface of polymeric micelles was modified through a maleimide-thiol coupling reaction to attach collagenase I and retinol (also known as vitamin A or VA). (B) The figure depicts a schematic representation of the proposed fate of four distinct polymeric micelles within an in vivo setting. The CRM/NIL, which resembles a nanodrill, exhibits the capability to infiltrate the collagen barrier and selectively targets activated HSCs. The process of internalizing CRM/NIL results in the liberation of NIL, leading to a decrease in the expression of TIMP-1, a metallopeptidase inhibitor. This subsequently promotes the degradation of collagen I, ultimately exhibiting a therapeutic effect against liver fibrosis. Reproduced with permission from Qian-Qian Fan et al. [152].