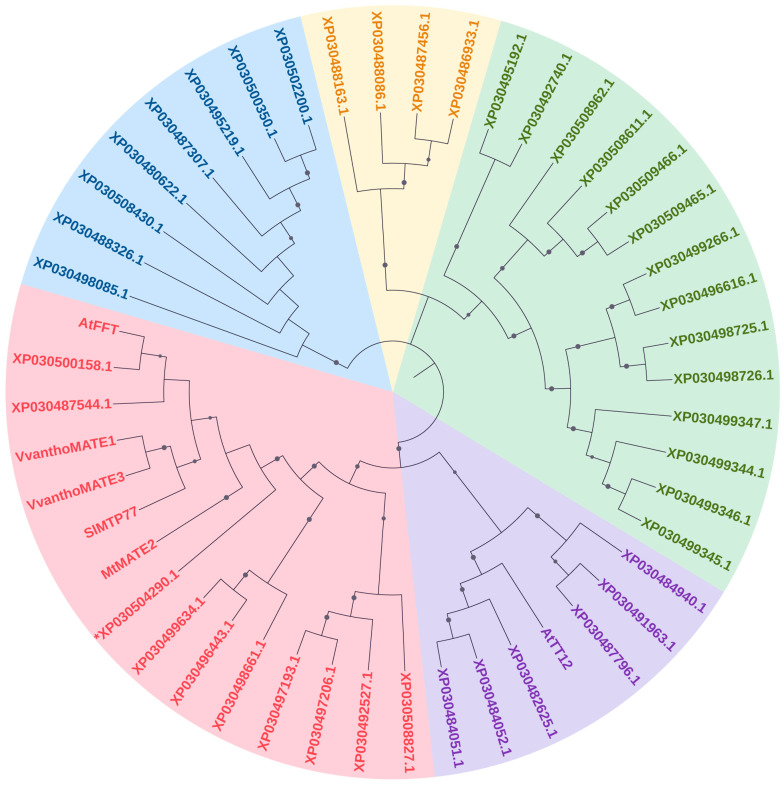
Figure 2.
Genome wide phylogenetic tree of the putative C. sativa MATE proteins. Different colors indicate major phylogenetic subgroups. Red and purple subgroups belong to the group/type II of MATE transporters according to [42] while the others are C. sativa MATE transporters. Previously described flavonoid transporters belonging to MATEs were included: Arabidopsis thaliana FFT (AT4G25640.2) and AtTT12 (AT3G59030.1); Vitis vinifera VvanthoMATE1, (NP_001290007.1) and VvanthoMATE3 (NP_001268037.1); Medicago truncatula MtMATE2, (XP_003592215.2); Solanum lycopersicum MTP77 (Solyc03g025220.2.1). The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method [16]. The optimal tree is shown. The evolutionary distances were computed using the p-distance method and are in the units of the number of amino acid differences per site. This analysis involved 48 amino acid sequences. All ambiguous positions were removed for each sequence pair (pairwise deletion option). There were a total of 742 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA11 [15]. The asterisk indicates the CsDTX35 (XP030504290.1) transporter. All amino acid sequences are reported in Supplementary Table S2. Bootstrap support values ≥ of 30% were indicated by grey circle on the tree branches.