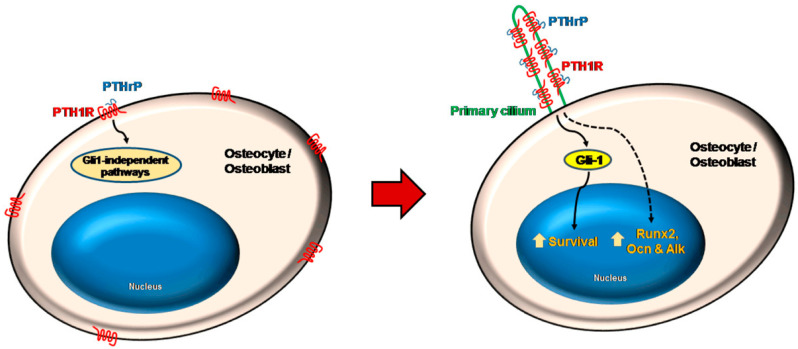
Figure 4.
Model depicting the pathways activated by PTHrP and inducing survival- and bone formation-related gene expression by mouse osteoblasts and osteocytes. Primary cilia- and Gli-1-dependent mechanisms are involved in the pro-survival action, whereas primary cilia-dependent and Gli-1-independent pathways mediate the overexpression of the osteogenic genes Runx2, osteocalcin (Ocn), and bone alkaline phosphatase (Alk). Reprinted from [34].