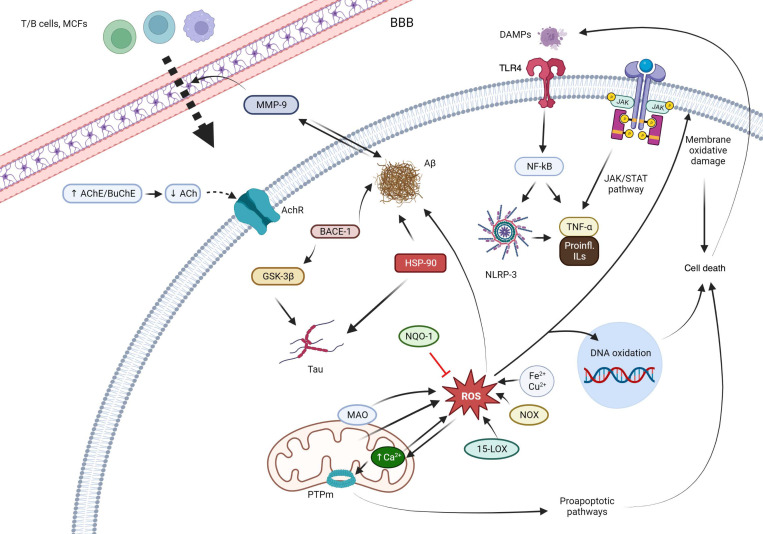
Figure 1.
Main mechanisms of action of the quinones described in this review. Abbreviations: T/B cells: the two main types of lymphocytes. BBB: blood brain barrier. AChE: acetylcholinesterase. BChE: butyrylcholinesterase. AChR: acetylcholine receptor. MMP-9: matrix metalloproteinase 9. Aβ: beta-amyloid protein. BACE-1: beta-secretase 1. GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta. HSP90: Heat-shock protein 90. NQO1: NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1. ROS: reactive oxygen species. MAO: monoamino oxidase. PTPm: mitochondrial permeability transition pore. 15-LOX: 15-lipooxygenase. NOX: nitric oxide. DAMPs: damage-associated molecular patterns. TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4. NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells. NRLP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3. JAK: Janus kinase. STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription. TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha. IL: interleukins.