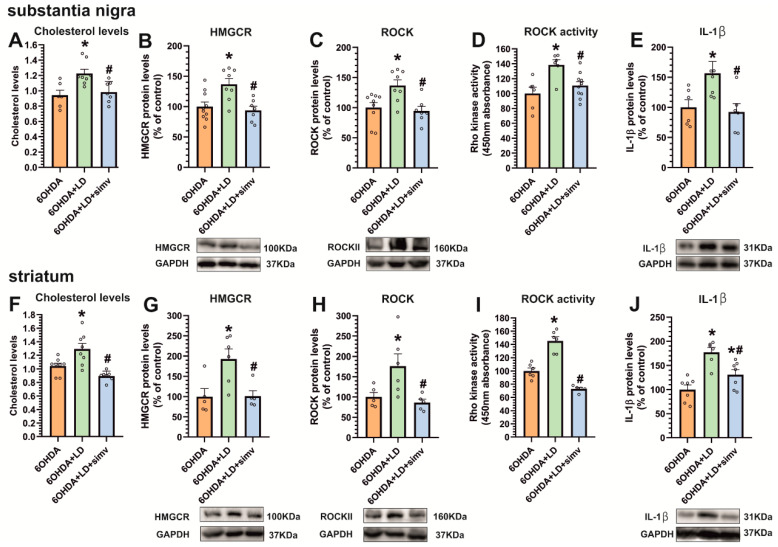
Figure 5.
Effect of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia and simvastatin on HMGCR, ROCK, and interleukin-1β. Dyskinetic rats chronically treated with L-DOPA 6 mg/kg (6-OHDA + LD, green bars) showed a significant increase in cholesterol levels (A,F) and in HMGCR protein levels (B,G), relative to 6-OHDA-lesioned rats (6-OHDA, orange bars) in the substantia nigra (A,B) and striatum (F,G). Moreover, dyskinetic animals showed a significant increase in ROCK protein levels (C,H), ROCK activity (D,I), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) protein expression (E,J) in both regions. The inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis by simvastatin (6-OHDA + LD + simv, blue bars) reduces dyskinesia, ROCK levels (C,H), ROCK activity (D,I), and IL-1β levels (E,J) in the striatum and substantia nigra. Data are means ± SEM. The results were normalized to the values of 6-OHDA-lesioned rats treated with vehicle. * p < 0.05, significant differences relative to 6-OHDA-lesioned rats; # p < 0.05 significant differences relative to L-DOPA-treated rats. One-way ANOVA and Holm–Sidak post hoc tests were used.