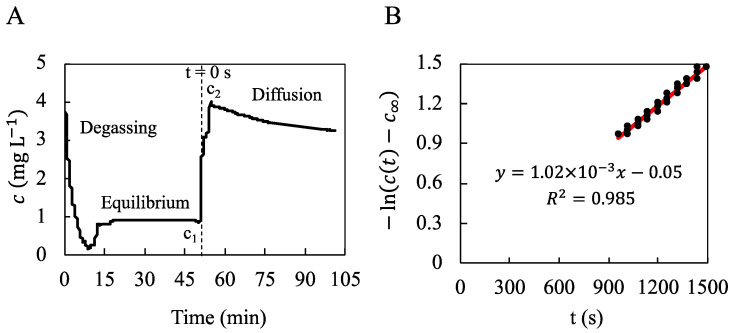
Figure 8.
Measurement of the oxygen concentration in a well-stirred reactor to determine the oxygen diffusion coefficient within the hydrogel. (A): The oxygen concentration (mg L−1) of the liquid phase in the well-stirred reactor was measured by an oxygen sensor as a function of time. N2-bubbling for 10 min allowed for degassing of the oxygen dissolved in the liquid phase (DPBS) until mg L−1 (“Degassing”). The well-stirred reactor was closed for 40 min until oxygen concentration stabilized at mg L−1 (“Equilibrium”). The liquid phase was quickly renewed with oxygen-saturated DPBS until the maximal oxygen concentration mg L−1. Then, the dissolved oxygen diffused from the liquid phase to the hydrogel for 50 min until the final oxygen concentration mg L−1 (“Diffusion”). (B): The diffusion coefficient was deduced from the linear regression of the quantity against the time between s and s. The origin of time is indicated in (A) and corresponds to the beginning of the stepwise concentration variation from to .