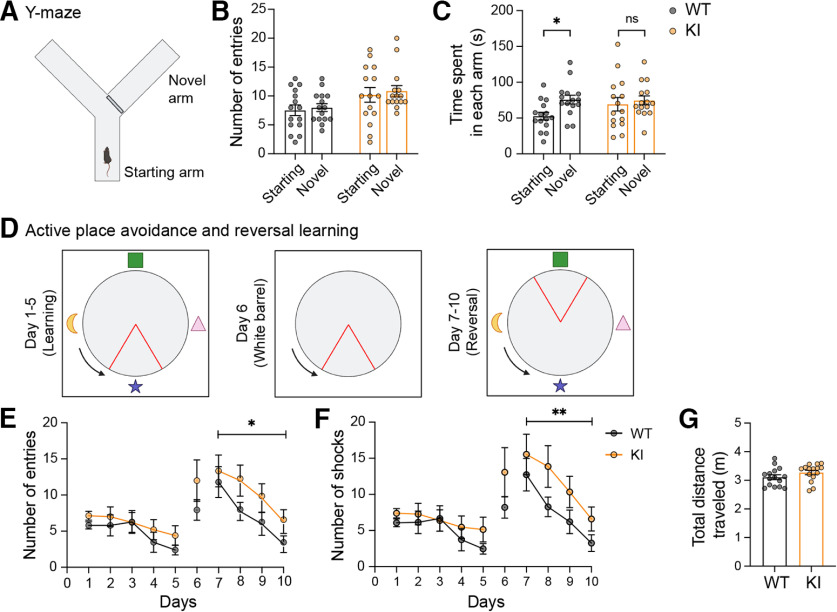
Figure 5.
GluA1 K868R mutant mice exhibit cognitive deficits. A-C, Measurement of short-term spatial working memory using the Y-maze with an initially blocked arm (A). Both WT and GluA1 KI littermates exhibited similar number of entries into the starting and the novel arms when opened (B). However, GluA1 WT, but not the KI mice, spent significantly more time in the novel arm (C). *p = 0.044 (two-way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparison test). D, Schematic representation of the experimental design for the active place avoidance and reversal learning tasks. The arena contained visual cues on each side of the wall. Blue arrows indicate arena rotation. Red triangles represent shock zone location. E, F, GluA1 KI mice displayed normal learning during the first 5 d but had significantly more entries into the shock zone (E) and shocks received (F) during reversal learning. F(1,112) = 6.033, *p = 0.016 (E) and F(1,112) = 7.278, **p = 0.0081 (F) (two-way ANOVA test). G, There was no difference in the total distance traveled during the task (Mann–Whitney test, p = 0.16). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 15 mice per group).