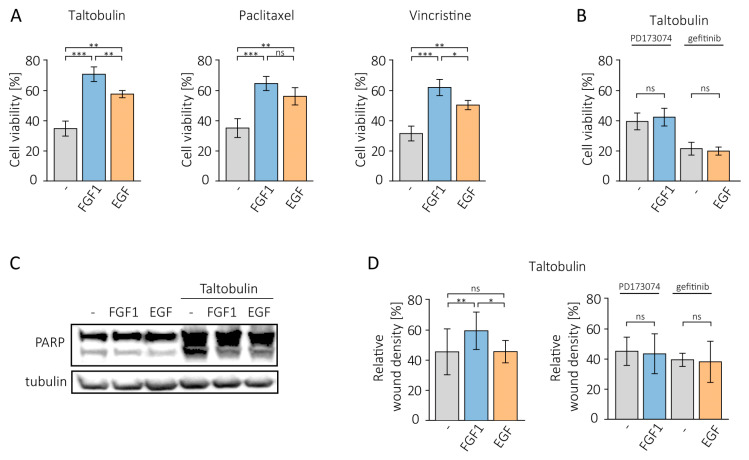
Figure 1.
Protective effect of FGF1 and EGF in MCF-7 cells treated with cytotoxic drugs. (A) The effect of FGF1 and EGF stimulation (10 ng/mL) on drug-induced cytotoxicity was investigated in MCF-7 cells treated with 5 nM TLT, 20 nM PTX or 10 nM VCR for 48 h. Cell viability was assessed using the alamarBlue assay. (B) The effect of growth factor receptor inhibition on FGF1 and EGF activity against taltobulin cytotoxicity was tested using 100 nM PD173074 and 10 µM gefitinib. (C) The anti-apoptotic effect of FGF1 and EGF against taltobulin-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 cells was assessed by evaluating PARP cleavage by Western blotting. Anti-PARP antibodies were used to detect PARP cleavage 24 h after treatment with 5 nM TLT in the presence or absence of 10 ng/mL FGF1 or EGF. (D) The effect of FGF1 and EGF on MCF-7 cell migration in the presence of 5 nM taltobulin was examined after 36 h using IncuCyte® Cell Migration and Invasion System. Normalization of relative wound density was based on both the density of cells in the wound area and the width of the wound itself and is expressed as a percentage of the wound area that was filled by migrating cells over time. Data are presented as mean values ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent experiments. Statistical significance: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, no significant differences indicated as ‘ns’.