Figure 1.
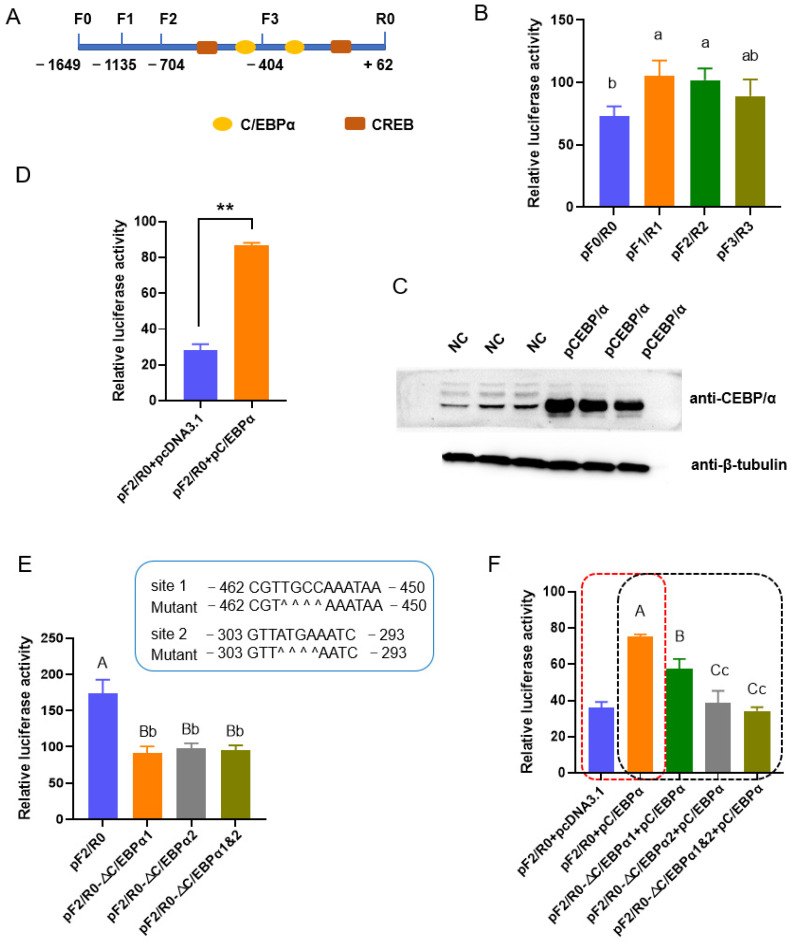
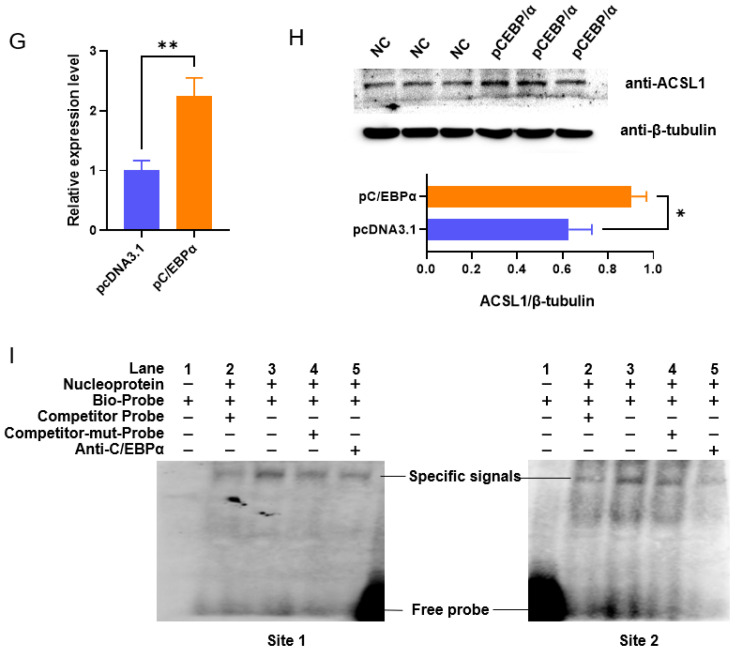
C/EBPα upregulates the expression of ACSL1 through binding to two motifs in the promoter. (A) Illustration of putative binding sites of C/EBPα and CREB in the promoter of ACSL1. F and R indicate forward and reverse primer, respectively; (B) Promoter activity of the upstream sequence and a series of 5′ truncated fragments; (C) Overexpression efficiencies of vectors containing the coding sequences of porcine C/EBPα as revealed with western blotting; (D) Ectopic C/EBPα enhances the promoter activity; (E) Deletion of the binding sites of C/EBPα decreases the promoter activity. Scheme for deleting the two binding sites of C/EBPα is given above, and ^ indicates a nucleotide deletion; (F) Effects of C/EBPα on the promoter activity were abolished by deletion of the binding sites; (G) Ectopic C/EBPα increases the mRNA level of ACSL1 gene; (H) Ectopic C/EBPα increases the protein level of ACSL1 gene; (I) C/EBPα binds to the putative motifs as revealed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Differences identified: *, a, b, and c, p < 0.05; **, A, B, C, p < 0.01.