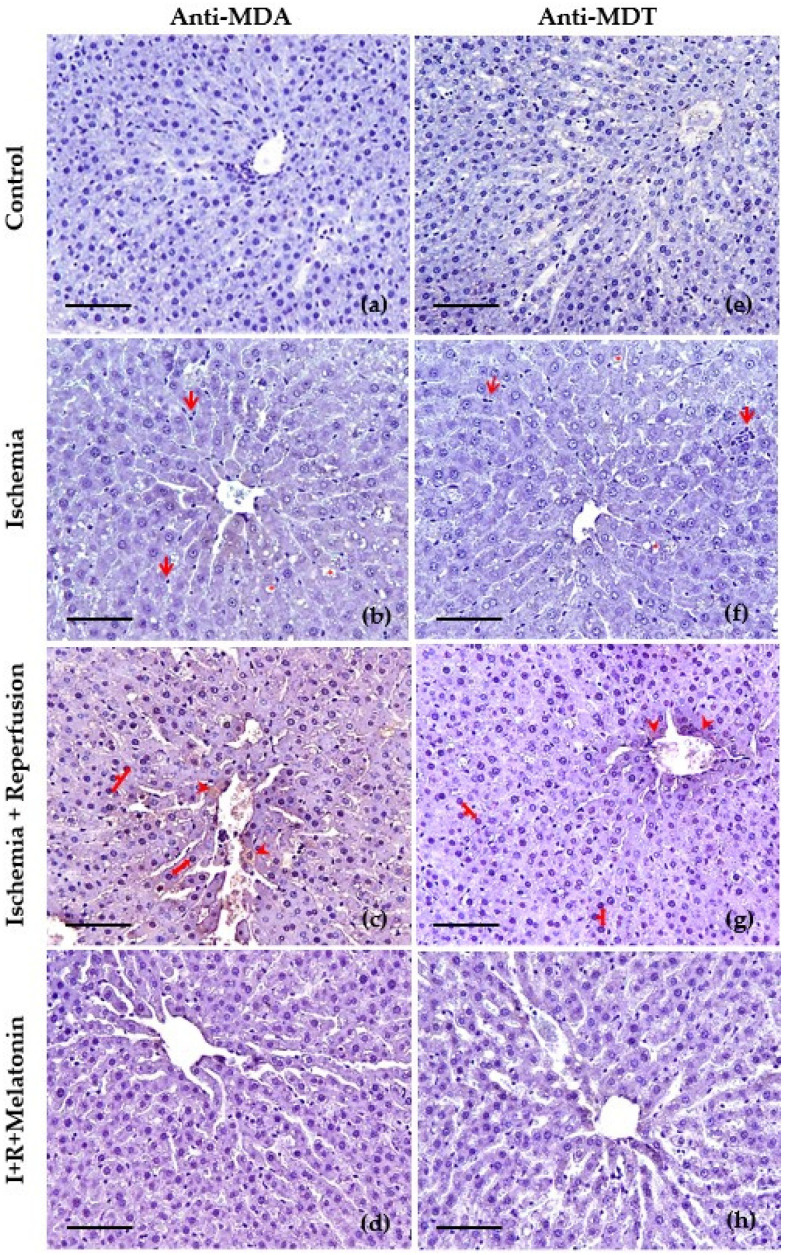
Figure 4.
Slides of hepatic tissues at the level of centrilobular vein obtained from control, exposed to ischemia (I), after reperfusion (R), and co-treated with melatonin (I + R + Melatonin). Images were captured at 200×. Scale bar: 100 μm. Immunohistochemical study using primary antibody to malondialdehyde (MDA) (a–d) and anti-dityrosine (MDT) (e–h). The main changes in ischemia (b,f) were hepatic vacuolization (red asterisks *), and leukocyte infiltration (red arrows), whereas the reperfusion indicated mainly hyperchromatic hepatocyte nuclei (red arrows) and oxidative damage (DAB+) (red arrowheads) especially to lipids (c) and to a lesser degree to proteins (g), in the proximity of the centrilobular vein (c,g), and in the hepatic cords (c). The concurrent administration of melatonin reduced the severity of these histopathological findings (d,h).