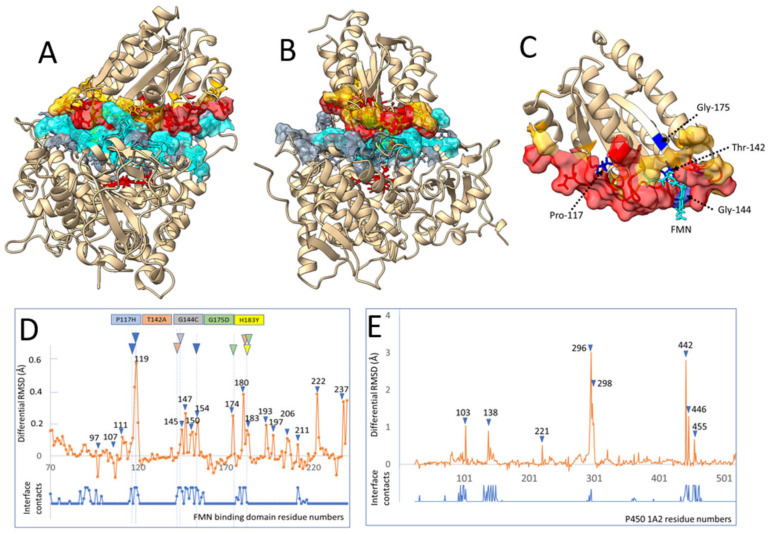
Figure 4.
Interaction between CYP1A2 and FD. (A,B) Views of the interface between CYP1A2 and the FD of the human reductase in two perpendicular orientations. Contacting residues (less than 3 Å) in more than 5 poses over 15 of alternatively modeled relaxed complexes and their surfaces are colored in blue and red for the CYP and the FMN domains, respectively. Less frequent contacts (1 to 4 over 15) in complexes are colored in grey and yellow, respectively. (C) Enlarged structure of the FD using the same color code. Five of the considered mutated residues interacting with interface are colored in dark blue and labeled as well as was the FMN cofactor. (D,E) Induced fit differential RMSD of FD side chains during binding to CYP1A2′s proximal side calculated (orange plot) as described in the experimental section. On top, a color code is given for five of the considered FD mutants examined. This code is reported in colored triangles at the corresponding amino acid positions. When multiple triangles are shown for a given mutant, alternate positions point to other residues that could be interacting with the mutated residue in the 3D structure. The number of interdomain contact hits among the 15 examined complex poses is overlaid (blue trace, see also Supplementary Figure S4).