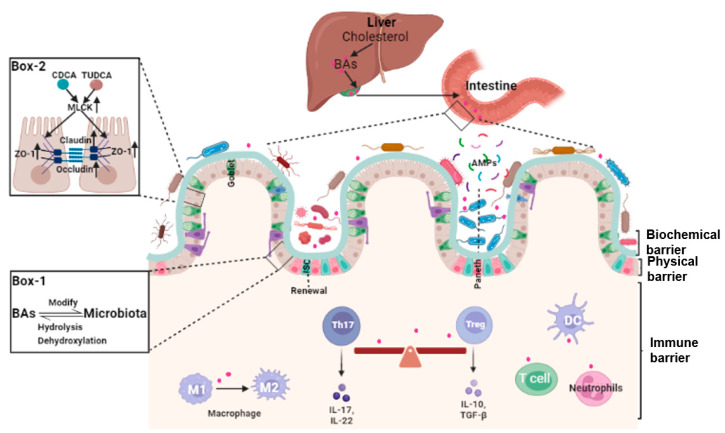
Figure 1.
The roles of bile acids in the homeostasis of the intestinal barrier. Bile acids (BAs) are synthesized in the liver, stored in the gallbladder, and secreted into the intestine. In the gut, bile acids modify the growth of gut microbiota. Reciprocally, bile acids are dehydroxylated and/or de-conjugated by the gut microbiota to form secondary or tertiary bile acids (Box 1). Bile acids such as CDCA and TUDCA are involved in the maintenance of the integrity of the intestinal barrier through affecting the expression of tight junction proteins (Box 2). Bile acids are also involved in modifying the gut microbiota and intestinal mucosal lamina propria local immune system. In this location, they regulate macrophage polarization, inflammatory T helper 17 (Th17) cells and regulatory T cell (Treg) cells, and dendritic cells (DCs).