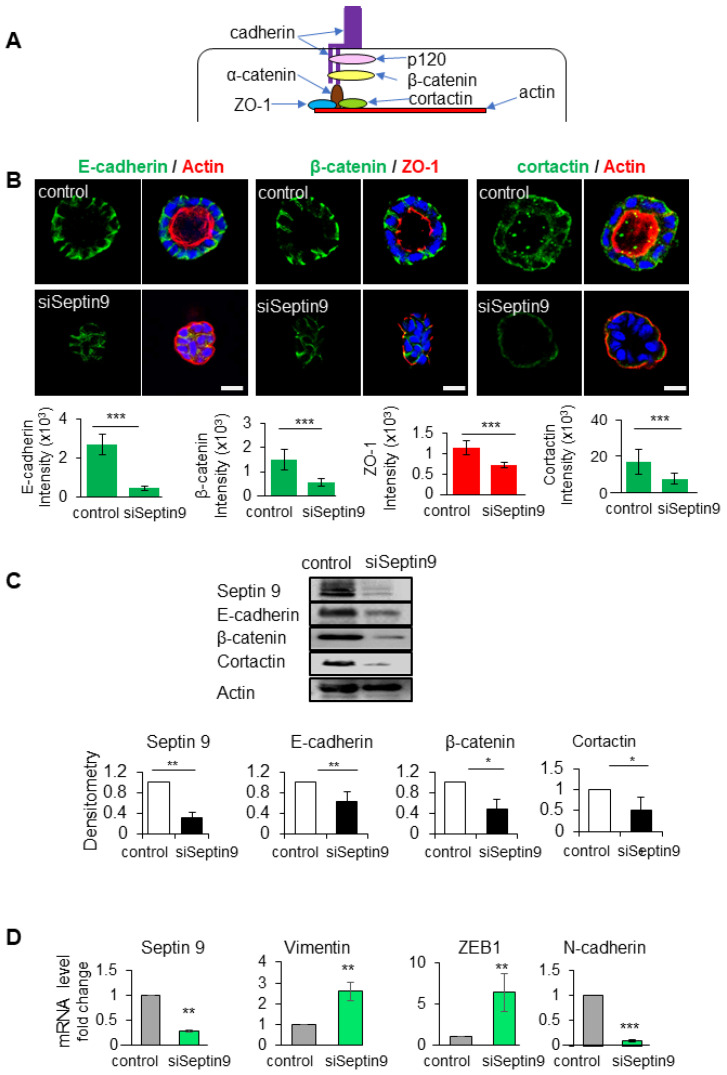
Figure 2.
Septin 9 regulates and impacts cell–cell adhesion and BM stability. (A) Schematic representation of the cell–cell adhesion structure. In the cytoplasm, the E-cadherin/catenin complex links to ZO-1, actin, and the actin-binding protein cortactin. (B) MDCK cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA (control) or with septin 9 siRNA for 24 h and plated on Matrigel for 4 days to form cysts and then stained for E-cadherin (green) and actin (red), β-catenin (green) and ZO-1 (red), and cortactin (green) and actin (red). A single confocal section through the middle of a cyst is shown. Quantification of the fluorescence intensity of each protein expression: E-cadherin (green), β-catenin (green), and ZO-1 (red). Scale bar 10 µm. (C) MDCK cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA (control) or with septin 9 siRNA (siSeptin9) for 24 h, then the medium was changed to continue grown on plates for 3 days. Cells were lysed and analyzed by Western blot to determine the expression of septin 9, E-cadherin, β-catenin, and cortactin proteins. (D) Another experiment; as in (C), qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of mRNA encoding septin 9, vimentin, N-cadherin, and ZEB1 in cells with control and septin 9 knock-down under 2D conditions. Data information: Data concern at least two replicates and cysts (n > 10) for 3D staining, three replicates for immunoblot and qRT-PCR. The statistical values are means ± s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.