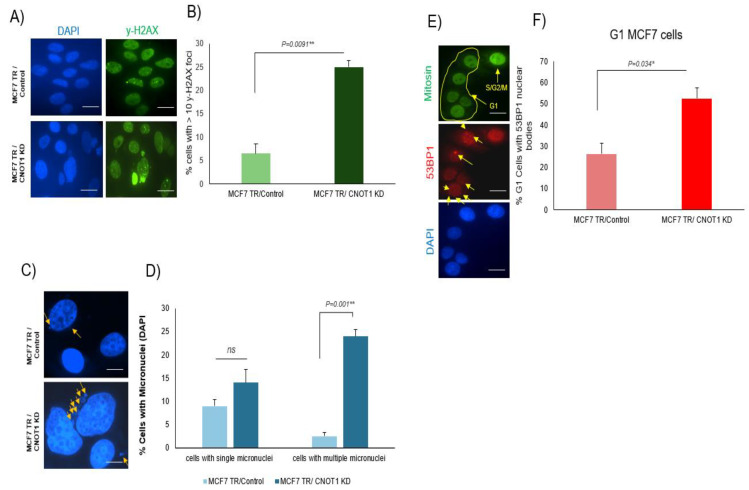
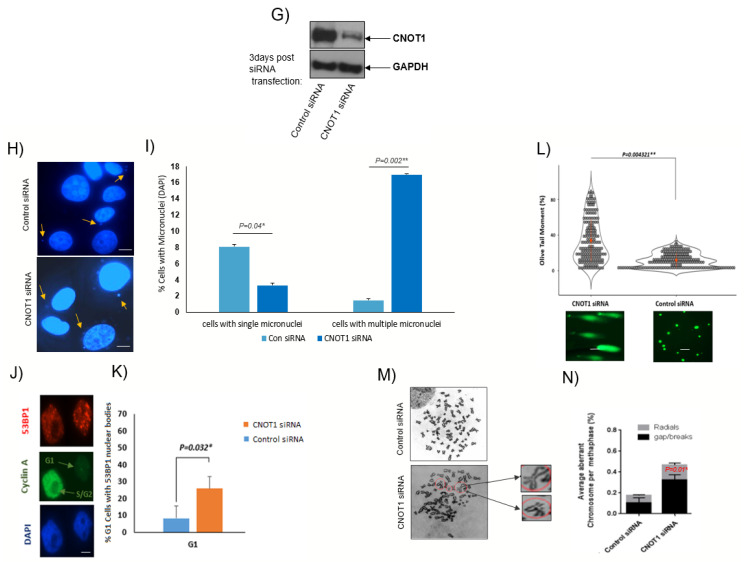
Figure 5.
Increased genome instability in CNOT1-depleted cells. (A,B) Quantification of cells with >10 γ-H2AX foci in MCF-7 cells 3 days post +/− 2 μg/mL DOX induction. (C,D,H,I) Quantification of siRNA treated HeLa cells and MCF TRCNOT1KD cells with micronuclei classified in two categories (single micronuclei per cell and multiple micronuclei per cell). Scale bars, 5 μm. (n = 3 independent experiments; >100 cells counted per repeat, mean ± SD, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 ). In (C,H) arrows indicate micronuclei. (E,F,J,K) Quantification of CNOT1 siRNA-treated HeLa and MCF TRCNOT1KD cells with 53BP1 nuclear bodies (indicated by arrows in central panel) in G1 positive control as judged by co-staining with either Cyclin A (J) or Mitosin (E) (in E, upper pane, and J, central panel, arrows indicate cells in a particular indicated phase of the cell cycle). (L) The level of DSBs, assessed using neutral comet assay, was performed 120 h post siRNA transfection in control and CNOT1-depleted HeLa cells. Dot plot of Olive tail moments was performed using RStudio statistical software (n = 3 independent experiments; >100 cells analysed per repeat, mean ± SD, ** p < 0.01 and). (M,N) Quantification of chromatid gaps and breaks per 100 metaphase spreads in control and CNOT1-depleted HeLa cells (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.005; n = 3). Scale bar = 50 µm. (G) Representative Western blot confirms the efficiency of CNOT1 depletion on day 3.