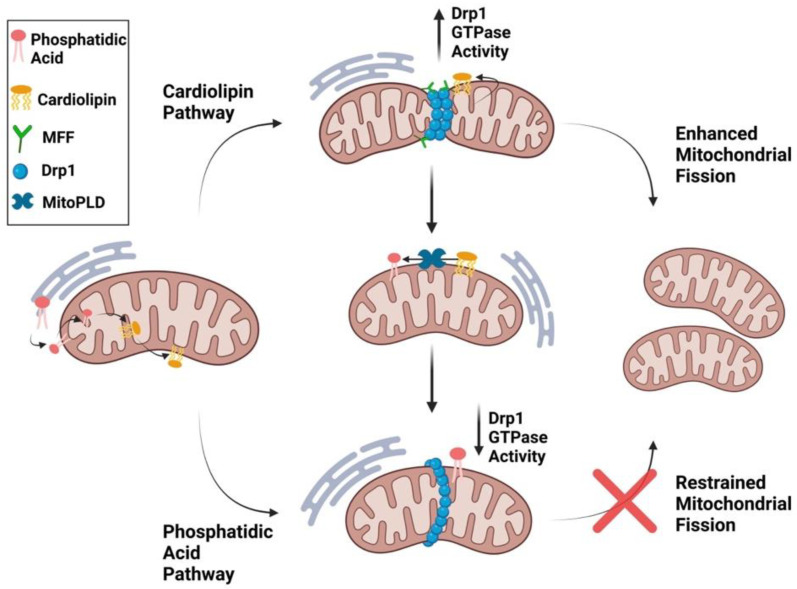
Figure 9.
Regulation of Mitochondrial Division by Phosphatidic Acid and Cardiolipin. Phosphatidic acid (PA) is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and transported to the mitochondrial outer membrane. A fraction of PA is transported to the inner mitochondrial membrane where it is converted to cardiolipin through cardiolipin synthase. Cardiolipin synthesized in the IMM is transported to the OMM where it interacts directly with Drp1 through its variable domain. This interaction stimulates Drp1 oligomerization and GTPase activity thereby enhancing fission. Cardiolipin-stimulated Drp1 GTPase activation is synergistically enhanced by MFF, suggesting that MFF acts with cardiolipin to potentiate mitochondrial fission. At the OMM, cardiolipin can be transformed back into phosphatidic acid by the mitochondrial OMM-localized enzyme, phospholipase D (MitoPLD). Phosphatidic acid inhibits Drp1-oligomerization-induced GTP hydrolysis, although it does not prevent Drp1 from forming its classic ring structure around the mitochondria.