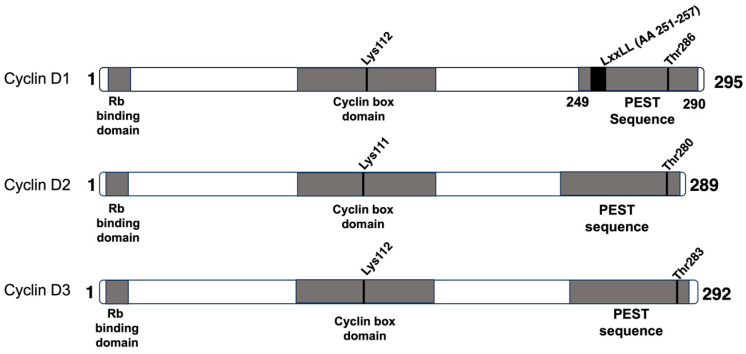
Figure 2.
Comparison of cyclins D1, D2, and D3. The three D-type cyclins share a number of conserved sequences and domains. The Rb-binding domain, located at the N-terminus, is responsible for binding the C-terminal helix of Rb when cyclin D is bound to CDK4/6. The cyclin box domain is a heavily conserved region of ~100 amino acids located in the N-terminus of each D-cyclin, which facilitates binding to CDK4/6. Mutagenesis of Lys112 (CCND1 and CCND3) and Lys111 (CCND2), in particular, abolishes binding to CDK4, demonstrating the residue’s essential role in mediating CDK-binding. The PEST sequence located at the C-terminus is required to mediate the degradation of cyclin D. Mutations at the Threonine phosphodegron site induce the stabilisation of cyclin D, resulting in increased progression of the cell cycle into the S-phase and genomic instability. CCND1 also possess an LxxLL motif, which mediates ligand-dependent interaction with nuclear receptors such as Erα.