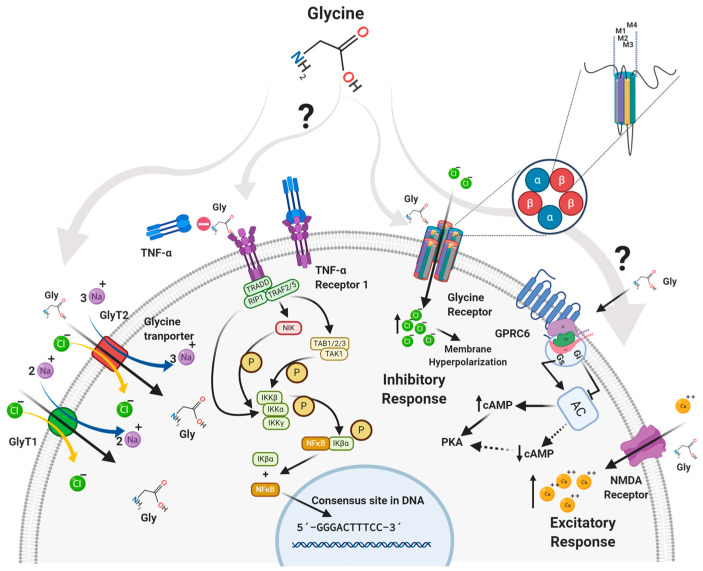
Figure 2.
Glycine targets and pathways. According to the International Union of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology (IUPHAR) glycine has different targets such as Natural/Endogenous Targets: glycine receptor (consisting of glycine receptor α1, α2, α3, α4 and β subunits), ionotropic glutamate receptors co-agonist (GluN1, GluN2A, GluN2B, GluN2C and GluN2D) and GPRC6 Receptor. Transporters moving this compound across a lipid membrane with proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1, vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter, Proton-coupled Amino acid Transporter 2, GlyT1, GlyT2, B0AT1, B0AT2, B0AT3, NTT4, sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 1, sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 2, sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 4, Sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 5 [27,28,29,30]. These may be the targets involved in the signaling by which glycine exerts its effect on the different cell lines of living organisms.