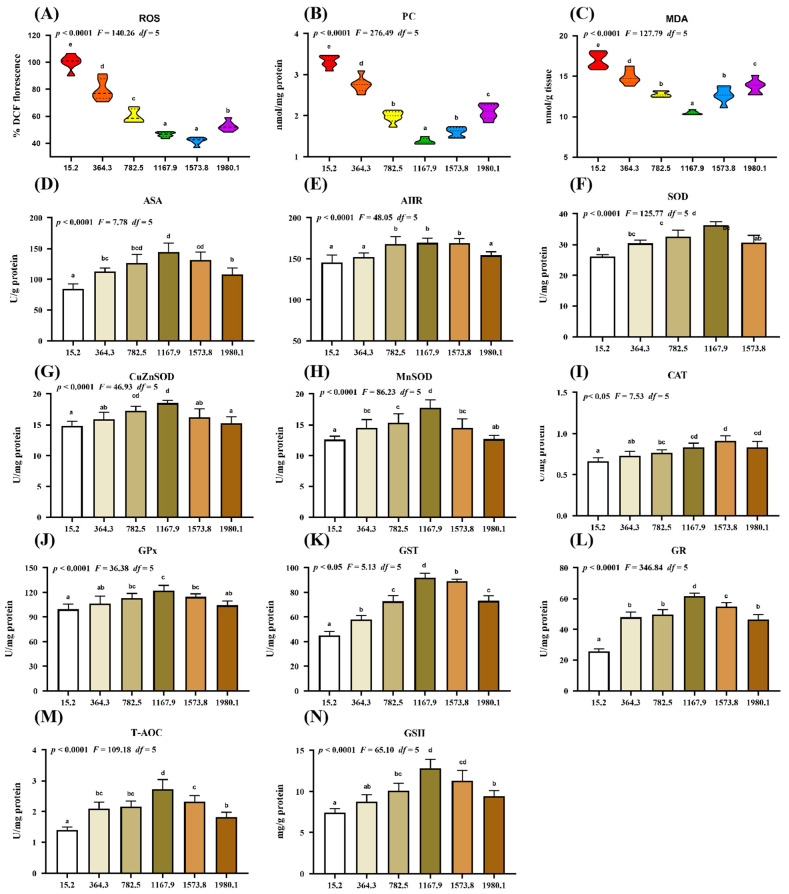
Figure 2.
Impact of dietary vitamin D on barrier function in the skin of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) after infection with A. hydrophila. (A–C) Biomarkers of oxidative damage: ROS, reactive oxygen species (% DCF fluorescence); MDA, malondialdehyde (nmol/g tissue); PC, protein carbonyl (nmol/mg protein). (D–N) Antioxidant-related parameters: ASA, anti-superoxide anion (U/g protein); AHR, anti-hydroxy radical (U/mg protein); SOD, superoxide dismutase (U/mg protein); CuZnSOD, copper/zinc superoxide dismutase (U/mg protein); MnSOD, manganese superoxide dismutase (U/mg protein); CAT, catalase (U/mg protein); GPx, glutathione peroxidase (U/mg protein); GST, glutathione S-transferase (U/mg protein); GR, glutathione reductase (U/mg protein); T-AOC, Total antioxidant capacity (U/mg protein); GSH, glutathione (mg/g protein). N = 6 for each vitamin D level. Different letters above bars indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).