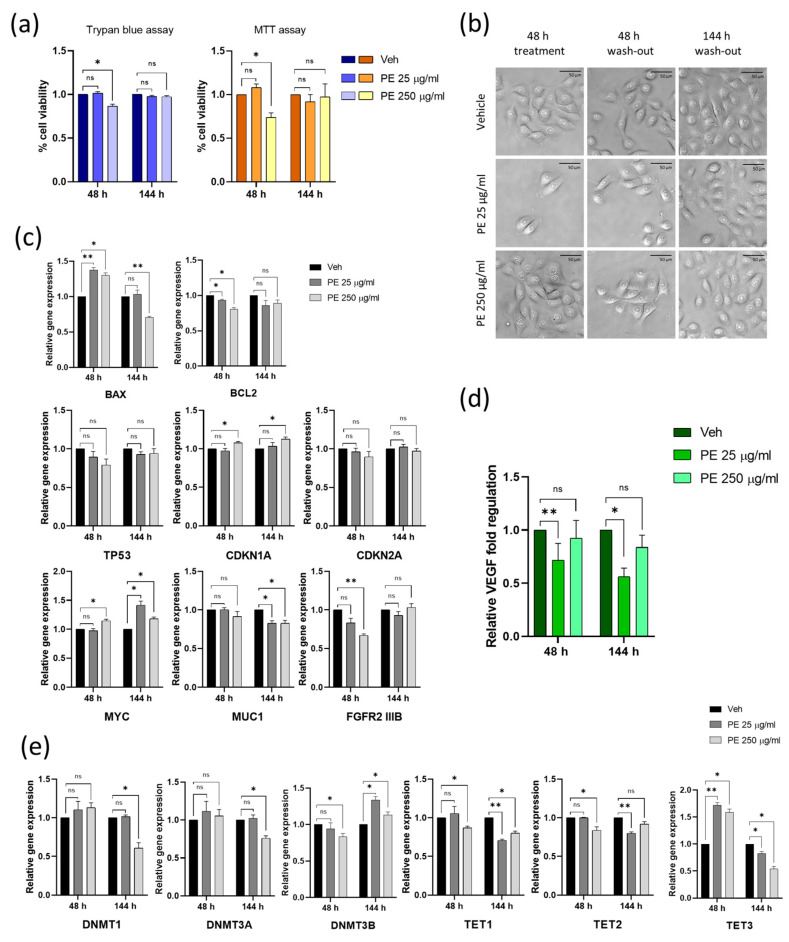
Figure 4.
Assessing the impact of discontinuous PE N/MPL exposure on cell viability, morphology, proliferation, inflammation, and epigenetic regulation in vaginal keratinocytes. (a) Graphs showing the percentage of viable cells upon 48 h of exposure to low and high concentrations of PE particles and 144 h post-wash-out obtained via Trypan blue and MTT assays. (b) Representative pictures of VK2 E6/E7 exposed to vehicle or PE N/MPLs for 48 h and 144 h after wash-out taken throughout the experimental points at 40× magnification. Scale bars are 50 μm. (c) Histograms for RT-qPCR analysis displaying a relative expression of apoptosis and cell cycle markers, and proliferation/differentiation-associated genes in VK2 E6/E7 exposed to vehicle or PE 25–250 μg/mL for 48 h and after 144 h wash-out. (d) Graphs showing relative fold regulation for VEGF concentrations detected in cell culture supernatants at 48 h of exposure to PE 25–250 μg/mL or vehicle and at 144 h from wash-out. (e) Relative gene expression of epigenetic regulation enzymes in vaginal keratinocytes exposed to PE 25–250 μg/mL or vehicle for 48 h and at 144 h post-wash-out. All the statistical analyses were conducted by unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test (n ≥ 3) with “ns” non-significant, * p ≤ 0.05 and ** p ≤ 0.005.