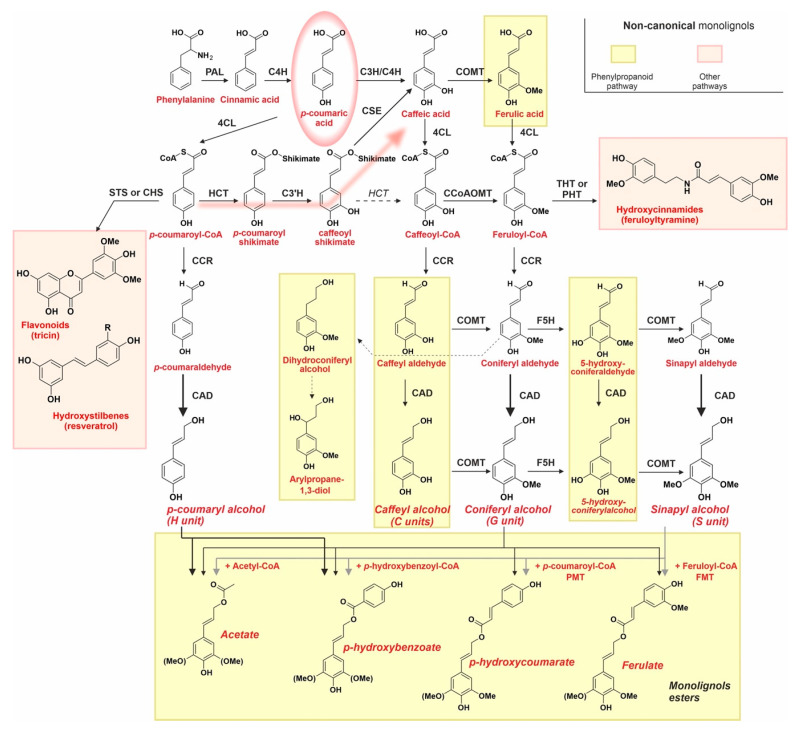
Figure 3.
The phenylpropanoid pathway leads to the biosynthesis of both canonical (no background) and non-canonical monolignols (light yellow background), while other non-canonical monolignols are produced through different but connected pathways (pink background). Phenylalanine (Phe) is sequentially converted to p-coumaryl alcohol (H unit) by phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H), 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (4CL), cinnamoyl-CoA reductase (CCR), and cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD). p-coumaric acid (red circle) is the ‘hinge’ of all these biosynthetic paths, since not only it is the precursor of p-coumaryl alcohol, but directly (via p-coumarate 3-hydroxylase, C3H) or through p-coumaryl-CoA (the so-called shikimate shunt (blurred red arrow). Enzymes involved: p-hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA:quinate/shikimate (HCT), p-coumaroyl shikimate 3-hydrolase (C3′H), and caffeoyl shikimate esterase (CSE)) also lead to the production of caffeic acid and then to that of all non-canonical phenylpropanoid monolignols. There, multiple and redundant pathways lead to coniferyl (G unit) and sinapyl alcohols (S unit) and involve caffeic acid O-methyltransferase (COMT), caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT), and ferulate 5-hydroxylase (F5H). Please note that among the non-canonical, phenylpropanoid-derived monolignols here we consider also compounds absent in Figure 2, such as ferulic acid (used in the formation of polysaccharide-lignin complexes, see later) or dihydroconiferyl alcohol, which is present in the lignin of CAD-deficient trees [65]. PMT: p-coumaroyl-CoA monolignol transferase (PMT). FMT: feruloyl-CoA with feruloyl-CoA monolignol transferase. For the non-phenylpropanoid pathway, hydroxystilbenes are produced through stilbene synthase (STS), and flavonoids are produced through chalcone synthase (CHS), whereas hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA:tyramine N-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase (THT) and hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA:putrescine hydroxycinnamoyltransferase (PHT), respectively, mediate the biosynthesis of diferuloylputrescine and of feruloyltyramine.