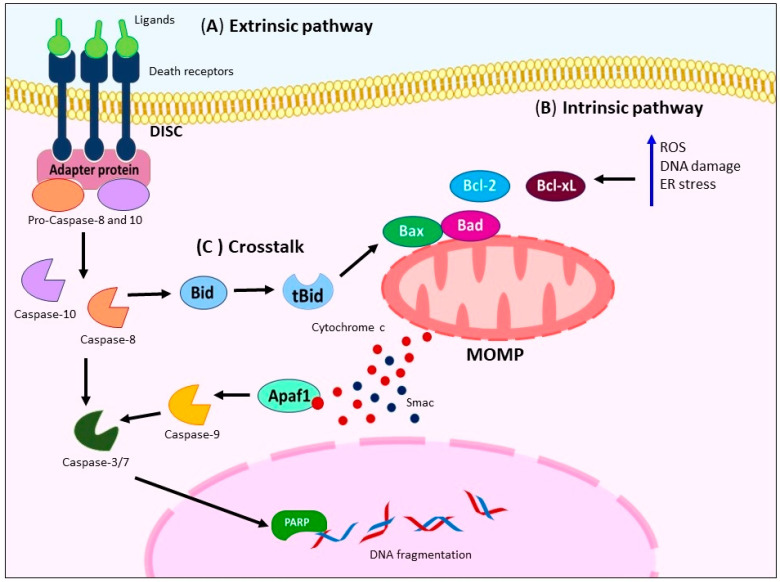
Figure 1.
Principal mechanism of apoptosis activation. (A) Activation of extrinsic pathway occurs through ligand binding to death receptors (FAS, TRAIL-R, or TNFR1), subsequently mediates bind of adapter proteins (FADD or TRADD) building DISC, activating caspase-8/-10 and -3. (B) Several stimuli trigger intrinsic pathway like cytokine deprivation, increase generation of ROS, DNA damage, and ER stress (blue arrow), causing MOMP that leads to the release of the mitochondrial proteins [cytochrome c (red dots), Smac (blue dots)], and subsequent activation of initiator caspase-9 and executioners caspases-3, -6, and -7 concluding in apoptosis. (C) There is crosstalk between the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways through the cleavage of caspase-8, which generates a tBid. tBid triggers MOMP, amplifying the apoptotic signal. FAS: Fas cell surface death receptor. TRAIL-R: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor. TNFR1: TNF receptor superfamily member 1A. FADD: FAS-associated death domain protein. TRADD: TNFR-associated death domain protein. DISC: Death-inducing signaling complex. ROS: Reactive oxygen species. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid. ER: Endoplasmic reticulum. MOMP: Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. tBid: Truncated form of Bid.