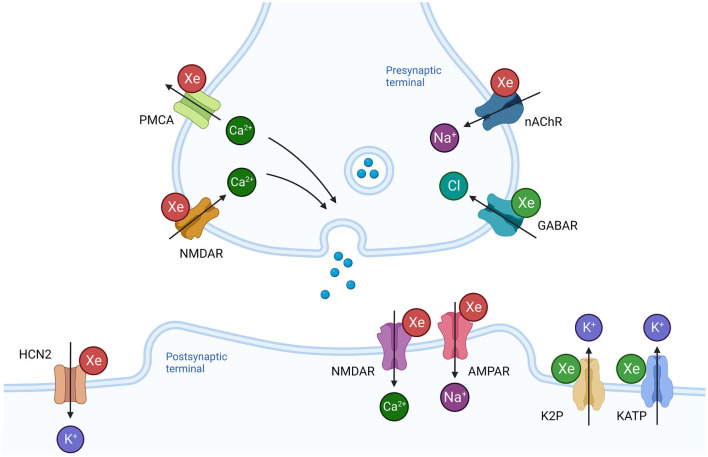
Figure 2.
Effects of xenon on synaptic transmission and neuronal excitability. Xenon influences a number of membrane bound proteins present in the presynaptic terminal that regulate neurotransmitter release. Inhibition of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) would prevent depolarization and reduce the probability of neurotransmitter release. Inhibition of presynaptic NMDAR and potentiation of GABAR would also reduce probability of neurotransmitter release. In contrast, inhibition of plasmalemmal calcium ATPase (PMCA) would promote release. Xenon reduces ionic current through NMDAR and AMPAR at the postsynaptic terminal. Potentiation of hyperpolarizing ionic currents through potassium channels (K2P, KATP) and inhibition of the depolarizing ionic current through the hyperpolarization activated cyclic nucleotide channel 2 (HCN2) reduce neuronal membrane excitability. Green Xe = xenon increases ionic current, Red Xe = xenon reduces ionic current. Created with BioRender.com.