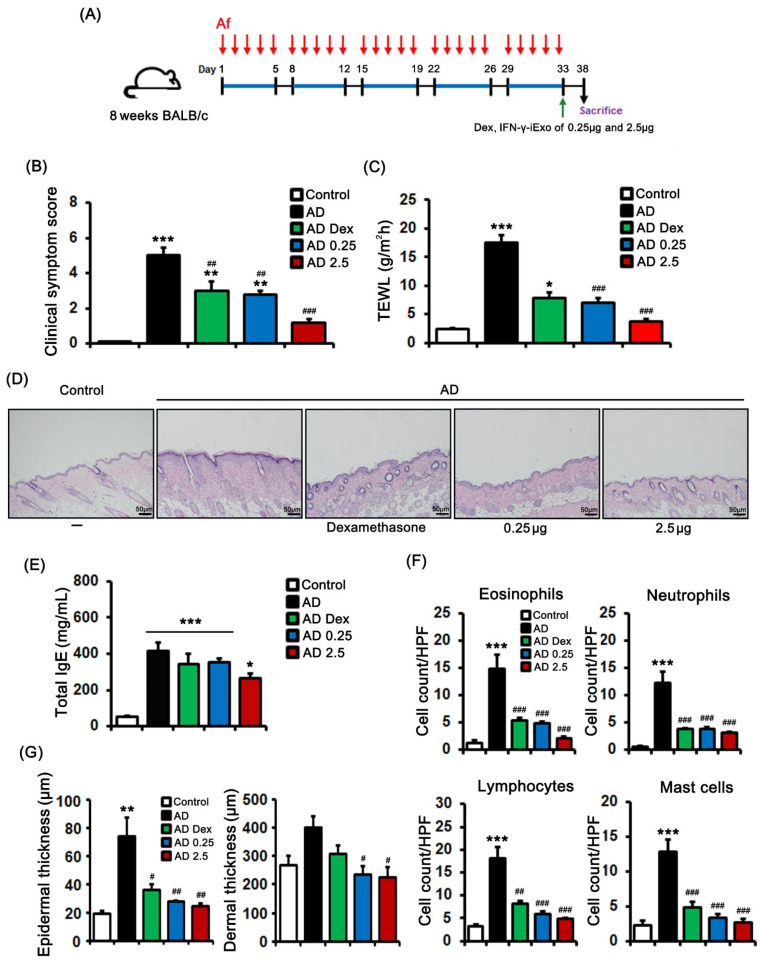
Figure 5.
Dose-dependent effects of IFN-γ-iExo in Aspergillus fumigatus (Af)-induced atopic dermatitis mouse model. (A) Schematic of the schedule for animal experiments. Aspergillus fumigatus (Af) extract (40 µg) was epicutaneously applied to the dorsal skin of the mice for five consecutive days per week for 5 weeks. Dexamethasone 0.1%, low dose IFN-γ-iExo (0.25 μg), or high dose IFN-γ-iExo (2.5 μg) was administered epicutaneously on the last day of the second series of Af applications. The mice were divided into five groups: control, AD, AD treated with 0.1% dexamethasone (AD Dex), AD treated with 0.25 μg of IFN-γ-iExo (AD 0.25), and AD treated with 2.5 μg of IFN-γ-iExo (AD 2.5). (B) Clinical symptom scores and (C) transepidermal water loss (TEWL) levels. (D) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the dorsal skin lesions. (E) Serum total IgE. (F) The numbers of eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes, and mast cells in the dorsal skin lesions. (G) Epidermal and dermal thickness of the dorsal skin lesion. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. control; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 vs. AD-PBS group.