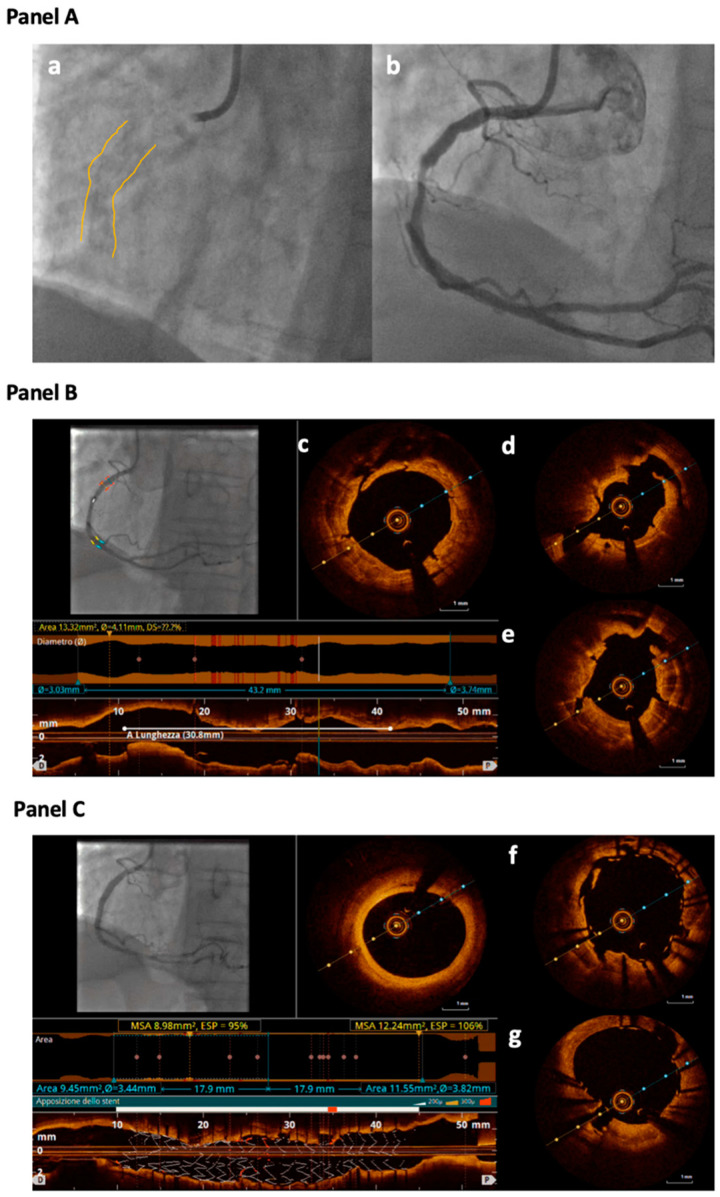
Figure 1.
Panel A: Angiographic view of a calcified stenosis located in the mid-Right Coronary Artery (RCA) (a,b); in the still frame without contrast (a) severe calcification is identifiable as radiopacity visible on both sides of the arterial lumen, as a double track (highlighted by yellow contours). Panel B: Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) evaluation of the RCA after treatment with 3.5 mm OPN balloon inflated at 30 atm. Different cross-sections show clear cracks into the calcific concentric plaque; small cuts not penetrating through the entire plaque are identifiable (c) as well as bigger cracks cutting the entire calcific plaque (d,e). Panel C: OCT evaluation of the RCA after stent deployment showing good struts apposition with cracks still evident behind the stent struts (f,g).