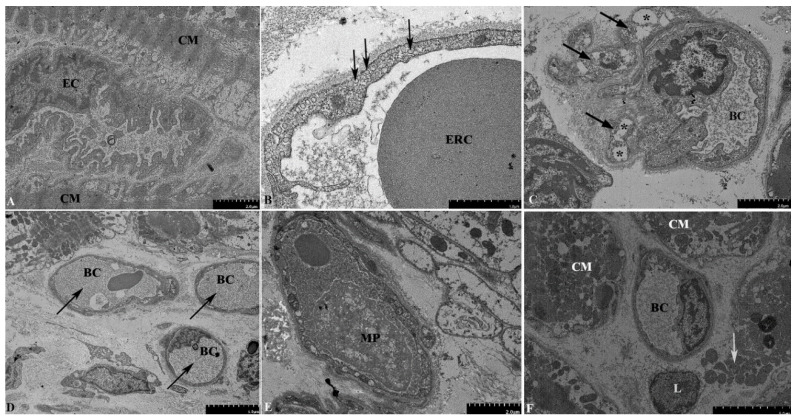
Figure 3.
Electron microscopy examination of the second EMB of the donor heart. (A) Irregularly shaped endothelial cells, with an indented luminal surface and irregular nuclei protruding into the lumen of the blood capillary. (B) A large number of vesicles in the cytoplasm of endothelial cells (arrows). (C) Pericyte processes (arrows) in close contact with the blood capillary. The processes contain vacuoles up to 1 µm in size (asterisks). (D) Obstruction of the capillary lumens by a fibrillar material of medium electron density, presumably fibrin (arrows). (E) Macrophages containing multiple phagocytic vacuoles in the capillary lumen. (F) Necrosis of cardiomyocytes, with a rupture of the plasma membrane and the release of intracellular organelles into the extracellular space (arrows). Abbreviations: EC—endothelial cell, CM—cardiomyocyte, BC—blood capillary, ERC—erythrocyte, MP—macrophage, L—lymphocyte.