Figure 3. Neurovascular coupling responses in the whisker sensory cortex corresponding to the peri‐ischemic area were reduced after cerebral ischemia.
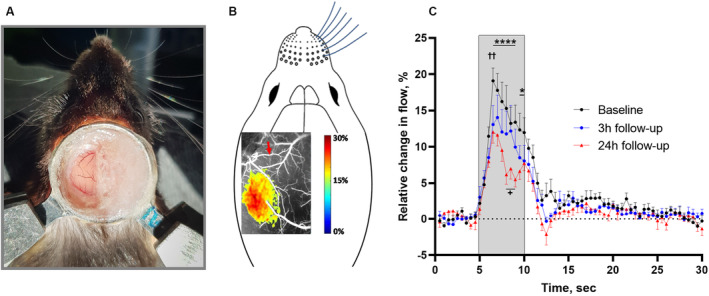
A, Image of the chronic cranial window preparation and the head fixation of the awake mouse 4 weeks after surgery. B, Representative laser speckle contrast image illustrating the local increase in blood flow in the whisker sensory cortex in response to air‐puff whisker stimulation at baseline. The red arrow indicates the artery that later was occluded. C, The neurovascular coupling response was reduced at the 3‐ and 24‐hour follow‐up compared with baseline. The gray area indicates the period when the 5‐second whisker stimulation was performed. Error bars=SE. Neurovascular responses were compared using 2‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's correction for multiple comparison. ✝✝ P<0.01 for 3‐hour follow‐up vs baseline; *P<0.05 and ****P<0.0001 for 24‐hour follow‐up vs baseline; + P<0.05 for 3‐hour vs 24‐hour follow‐up; n=6.
