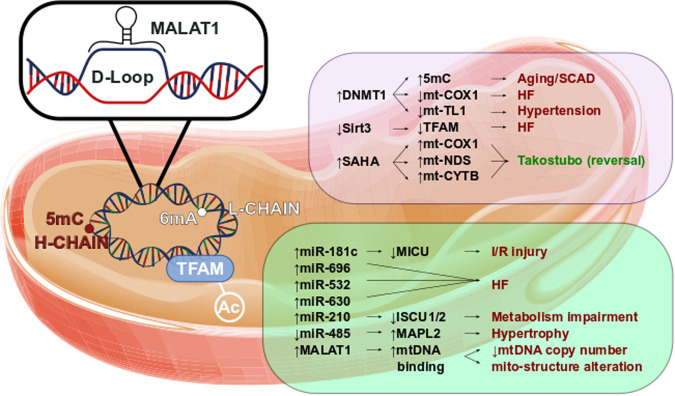
Figure 2.
Mitoepigenetics of cardiovascular diseases. Several epigenetic modifications might occur in mitochondrial matrix. The mt-DNA methylation occurs mainly in Adenine of L-chain. However, the 5mC in H-chain has been found to have a regulatory function. In fact, the increase of 5mC has been observed in aged mitochondria as well in mitochondria leucocyte of SCAD patients. In parallel, high level of 5mC in mt-COXQ and in mt-TL1 promoters triggers the HF and hypertension. Additionally, the retains of TFAM acetylation, caused by the decrease of Sirt3 activity, has been observed in HF. Little is known of SAHA effects in mitochondrial regulation, however we might suppose that SAHA modulates the expression of mt-COX1, mt-NDS, and mt-CYTB contributing to Takotsubo disease reversion. Pivotal roles have also been observed in mitochondrial ncRNA regulation. Higher level of miR-181c is leaded to the worsening of I/R injury as well the up-regulation of miR-696, miR-532 and miR-630 triggers the HF. The impairment of metabolism has been associated to the increase of miR-210 through the repression of ISCU1/2. The down-regulation of mitochondrial miR-485 increases MAPL2 expression which stimulates the hypertrophic growth. lncRNAs are involved in CVD too. In fact, MALAT1 has been found to bind the D-Loop of mt-DNA inhibiting the synthesis of new mt-DNA. The reduction of mt-DNA copy number reflects the alteration of mitochondrial structure and the impairment of the oxidative phosphorylation.