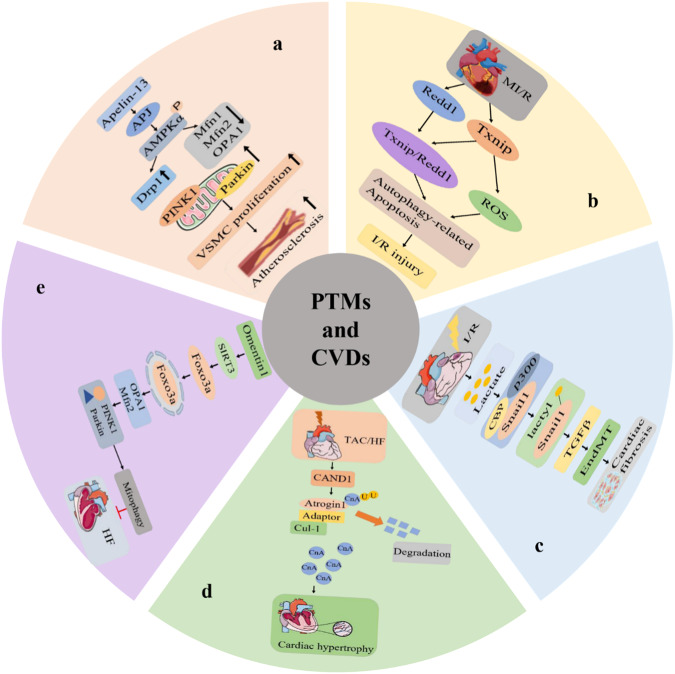
Fig. 3. PTMs involve some mechanisms in CVDs.
a Schematic diagram of PINK1/Parkin‐dependent mitophagy is responsible for apelin‐13‐induced human aortic VSMC proliferation and atherosclerotic lesions. b Schematic diagram of TXNIP-Redd1 expression is a novel signaling pathway that contributes to I/R injury by exaggerating excessive autophagy during reperfusion. c Schematic diagram of lactate-induced EndoMT after MI. d Schematic diagram depicting the proposed signaling mechanisms underlying the effects of CAND1 in the setting of cardiac hypertrophy. e The schematic of omentin1 ameliorated ischemia-induced HF via maintaining mitochondrial dynamical homeostasis and mitophagy. VSMC vascular smooth muscle cells, AS Atherosclerosis, PINK1 phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)‐induced kinase 1, AMPK Adenosine monophosphate‐activated protein kinase, Drp1 dynamin‐related protein 1, Mfn1 and Mfn2 mitochondrial membranes mitofusin 1 and 2, OPA1 optic atrophy 1, Apelin a bioactive peptide and the ligand of the G protein-coupled receptor APJ, parkin E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin, Omentin1 a novel adipokine, Foxo3a forkhead box O3a, CAND1 Cullin-associated and neddylation-dissociated 1 protein, EndoMT Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition, TGF-β transforming growth factor–β, Snail a zinc finger transcription factor, Cul1 ubiquitin-protein ligase, CnA calcineurin, Atrogin-1 E3 ubiquitin ligases, Adaptor adaptor protein.