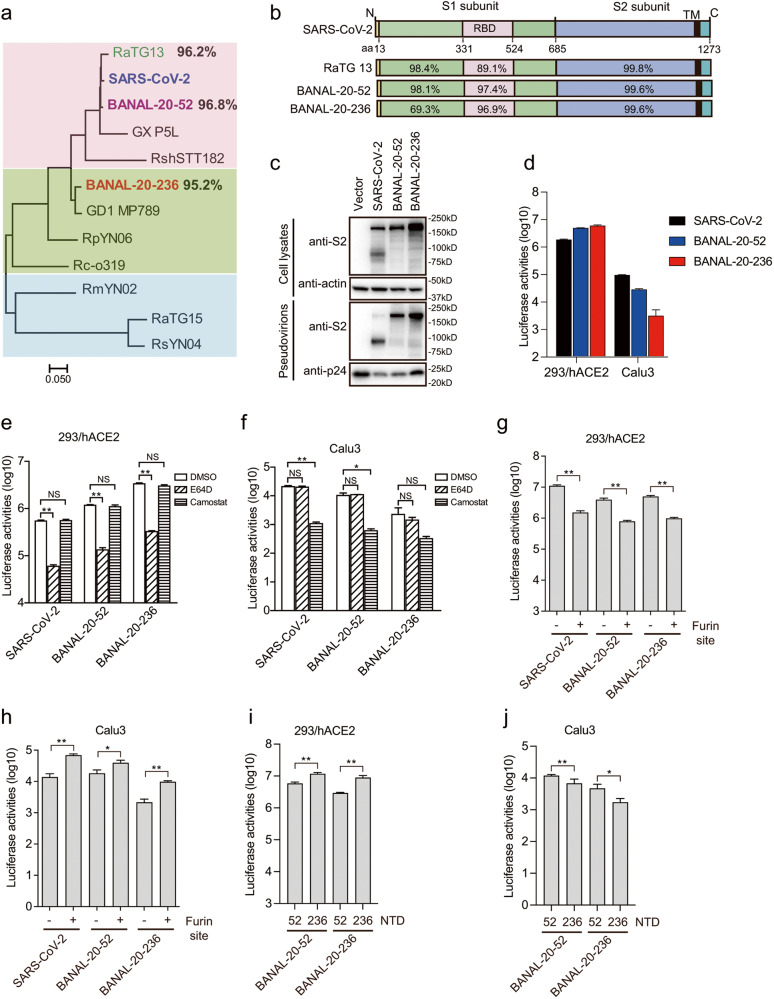
Fig. 1. Characterization of S proteins of BANAL-20-52 and BANAL-20-236 on virus entry.
a Phylogenetic tree of the S proteins of SARS-CoV-2-related CoVs. The maximum-likelihood tree was produced using MEGAX software, based on the alignment of amino acid sequences of S proteins. b Schematic diagram of S proteins of the indicated CoVs and the amino acid sequence identities of each region are shown. RBD receptor binding domain, TM transmembrane domain. c Western blotting analysis of the S proteins of SARS-CoV-2, BANAL-20-52, and BANAL-20-236 in cells lysates and pseudovirions using rabbit polyclonal anti-SARS-CoV-2 S2 antibody 40590-T62. β-actin and gag-p24 served as loading controls. d Entry of SARS-CoV-2 S, BANAL-20-52 S and BANAL-20-236 S pseudovirions on indicated cell lines. 293/hACE2 cells, 293 cells stably expressing human ACE2. e, f Inhibition of entry of SARS-CoV-2 S, BANAL-20-52 S, and BANAL-20-236 S pseudovirions into 293/hACE2 (e) and CaLu3 (f) cells by a broad-spectrum cathepsin inhibitor, E64D, or a serine protease inhibitor, camostat. g, h Transduction of 293/hACE2 (g) and CaLu3 (h) cells by SARS-CoV-2, BANAL-20-52, and BANAL-20-52 S proteins with or without a furin cleavage site pseudotyped lentiviral particles. i, j Transduction of 293/hACE2 (i) and CaLu3 (j) cells by chimeric BANAL-20-52 and BANAL-20-236 S pseudovirions. Data are represented as means ± SD from at least triplicates. P-values in e–j are calculated by unpaired two-sided Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, P > 0.05.