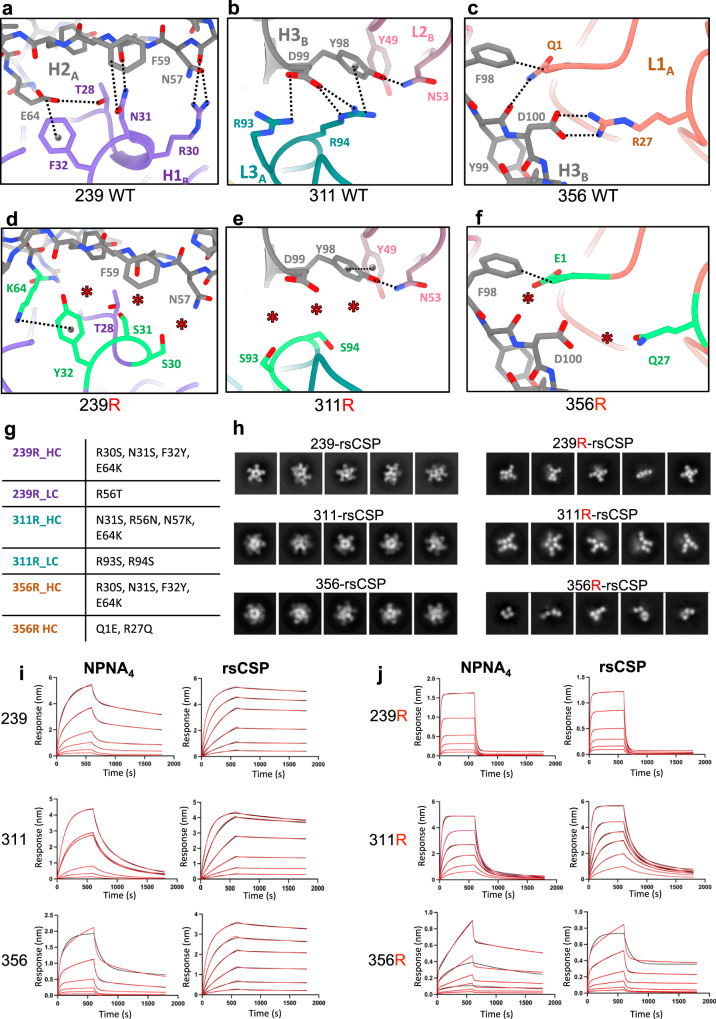
Fig. 4. Structural and functional effects of mutagenesis of the homotypic interface.
a–c Key, somatically mutated homotypic interactions observed in cryo-EM structures of 239 (a), 311 (b), and 356 (c). Dashed lines indicate observed homotypic contacts. d–f Anticipated structural impact of reversion of these residues to germline identities. Mutant structures were calculated from WT cryo-EM structures in Coot and are not experimental. Red asterisk indicates loss of homotypic contacts. Dashed lines indicate potential germline-encoded homotypic contacts. g List of germline-reverted constructs. Mutations are listed on right, using Kabat numbering system. h 2D class averages from NS-EM of WT and mutant Fab complexes with rsCSP. Mutant classes on right clearly show loss of well-ordered helical structure observed with WT Fabs. i, j Binding curves from BLI for WT (i) and mutant (j) Fabs. NPNA4 and rsCSP were immobilized on Streptavidin and Ni-NTA sensors, respectively, and binding of each of the Fabs were measured at 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, and 200 nM. Curves were fit with a 2:1 binding model shown in red. nm nanometers. See also Fig. S6. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.