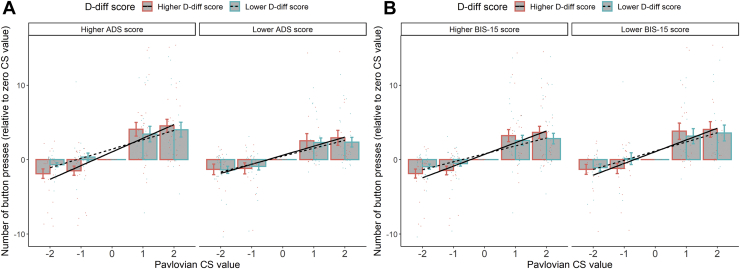
Figure 2.
(A) Patients with higher Alcohol Dependence Scale (ADS) scores had a stronger association between alcohol approach bias (i.e., D-diff score) and the Pavlovian-to-instrumental transfer effect. (B) Patients with higher Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-15 (BIS-15) scores showed a stronger association between alcohol approach bias and the Pavlovian-to-instrumental transfer effect. Alcohol approach bias, ADS score, and BIS-15 score in this figure were all transferred to factors with two levels with a median split for illustration. Group means and SEMs are shown with bars and error bars. Individual values (mean number of button presses) are represented by colored dots.