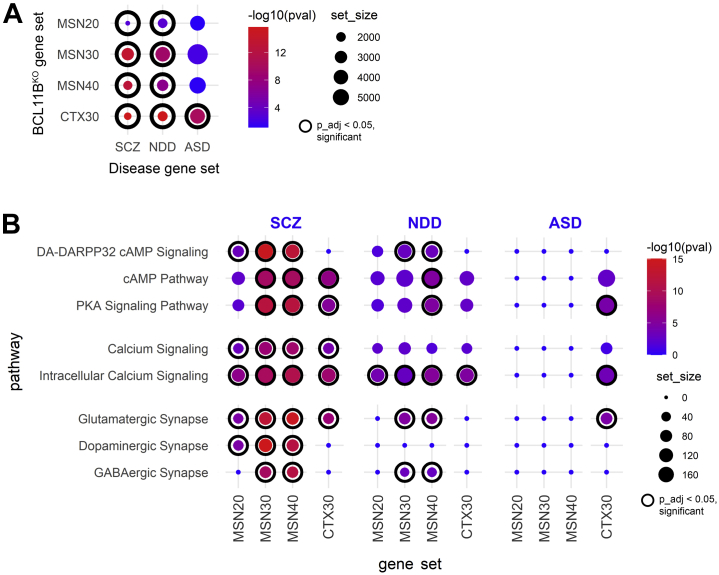
Figure 5.
A role for BCL11B-dependent DA-DARPP32 and cAMP-PKA-calcium signaling axis in the pathogenesis of psychiatric disorders. (A) BCL11B-regulated genes in MSNs are significantly enriched for SCZ and NDD risk genes but not ASD risk genes at all stages of differentiation, while CTX30 differentially expressed genes were enriched for all disease risk genes. p values were calculated from Fisher’s exact test followed by Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. (B) BCL11B-dependent signaling pathways in MSNs are predominantly enriched for SCZ but not NDD risk variants, while pathways in CTX neurons were enriched for both SCZ and ASD risk genes (full gene set lists are presented in Table S7). In graphs, dot size corresponds to gene set size, dot color corresponds to −log10(pval), where p_adj < .05 dot is framed inside a black circle. See also Figures S5 and S6 and Tables S5–S7. ASD, autism spectrum disorder; CTX, cortical glutamatergic; DA, dopamine; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; KO, knockout; MSNs, medium spiny neurons; NDD; neurodevelopmental disorder; p_adj, p adjusted; PKA, protein kinase A; SCZ, schizophrenia.