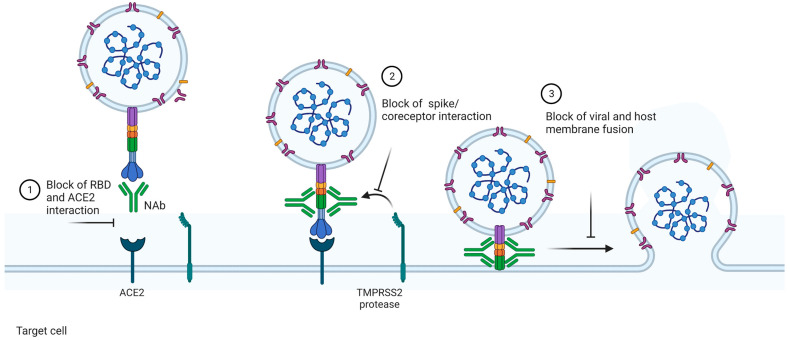
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of action of neutralizing antibodies (NAbs). NAbs can act via different mechanisms to neutralize viruses. In this example, we focus on the neutralizing mechanisms involving SARS-CoV-2. (1) NAbs can bind to the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the spike glycoprotein from the viruses and block the contact between it and the ACE2 expressed in the surface of the host cells. Since the viral entry is dependent on this ligation, the infection is blocked. NAbs can also recognize epitopes outside the RBD. In this case, the contact between the spike and ACE2 is not avoided. However, the following mechanisms essential for viral entry are blocked. Via this mechanism, (2) Nabs inhibit the interaction between the TMPRSS2 protease and spike cleavage, essential for the touch of viral and host membranes, or (3) block the membrane fusion and, thus, viral infection. The image was created with https://www.biorender.com/ (accessed on 10 January 2023).